Author Archives: Chris Bergh
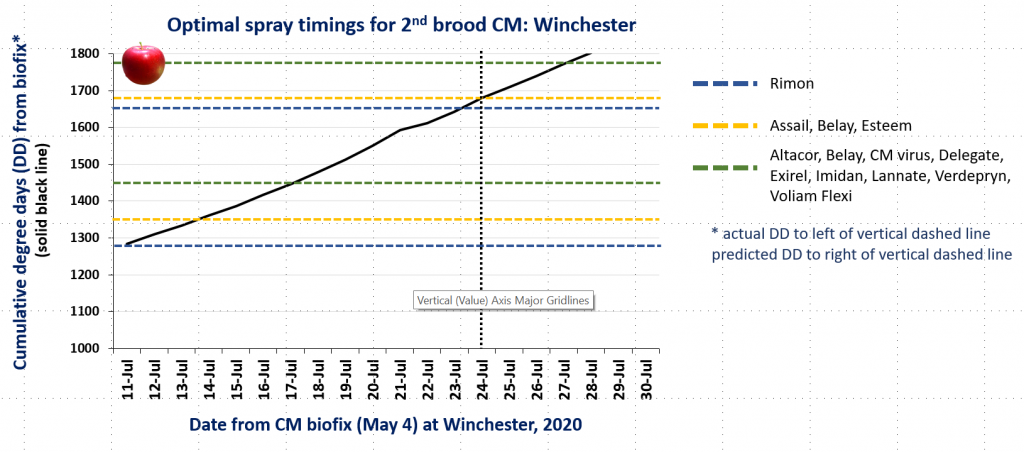
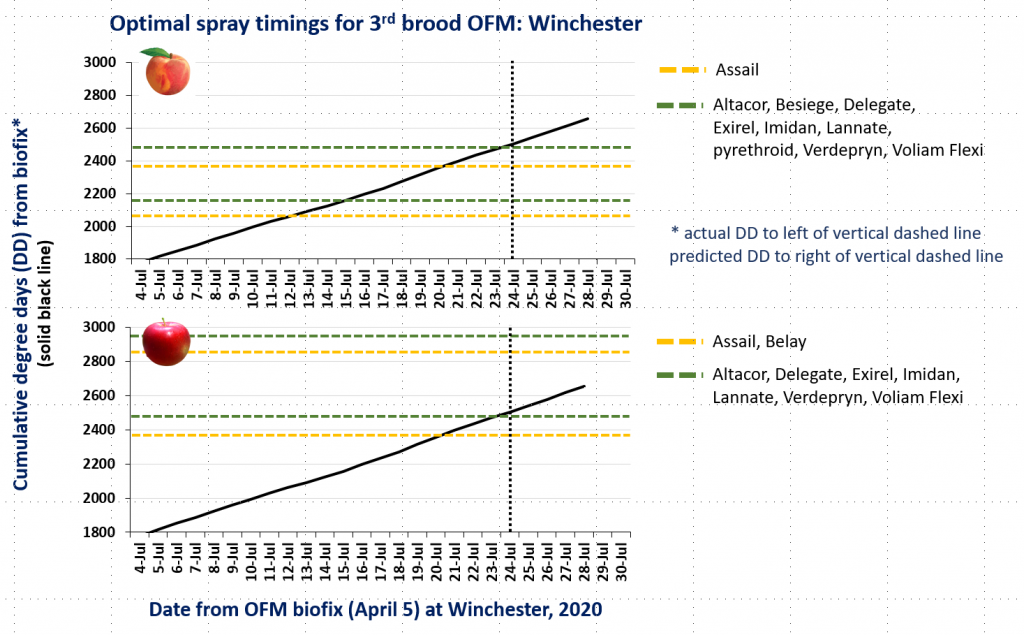
CM and OFM Degree Days and Optimal Spray Timing, 7.23.20
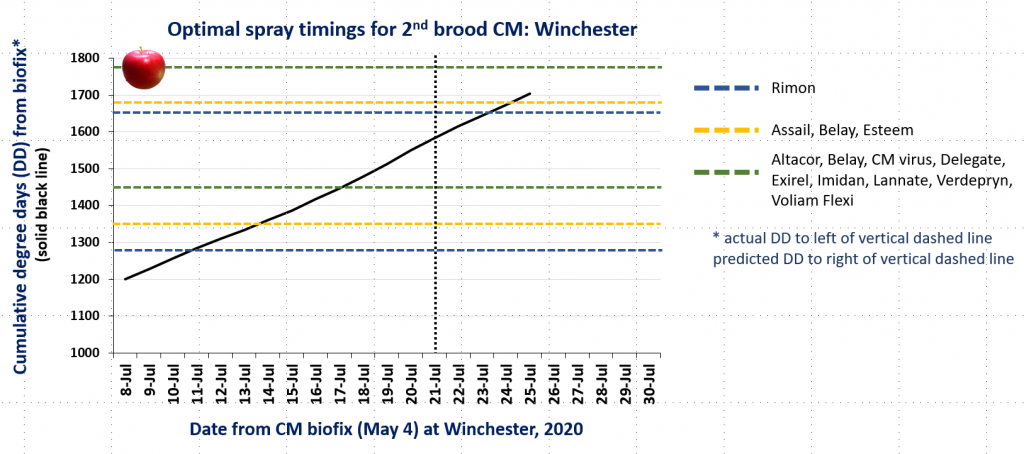
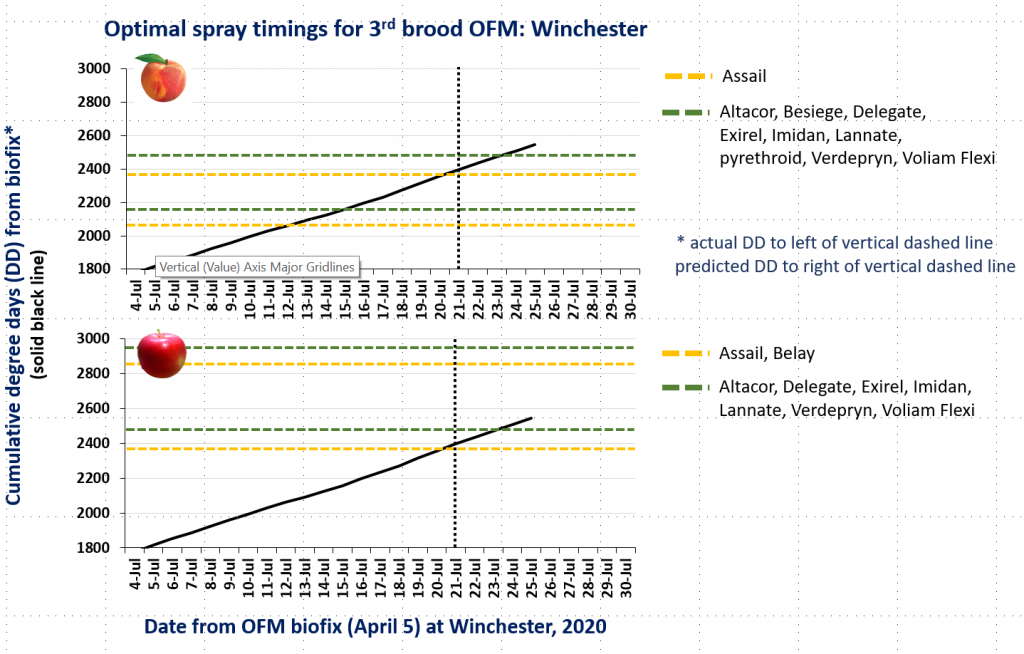
CM and OFM Degree Days and Optimal Spray Timing, 7.20.20
Section 18 Emergency Exemption approved for dinotefuran against brown marmorated stink bug
On July 15, 2020 the EPA approved the renewal of a Section 18 Emergency Exemption for use of the neonicotinoid insecticide, dinotefuran, against brown marmorated stink bug in pome and stone fruit crops in Virginia. Growers from the other States that have previously participated in this Section 18 should contact their State Department of Agriculture regarding the status of this petition. The two products included in this exemption are Venom Insecticide and Scorpion 35SL Insecticide. Per application, Venom can be used at rates between 4.0 and 6.75 oz of product per acre (0.179 to 0.302 lb active ingredient) and Scorpion at 8.0 to 12.0 fl oz of product per acre (0.203 to 0.304 lb active ingredient). Restrictions include a maximum of two applications per season, a seasonal maximum of 0.608 lb active ingredient per acre (regardless of product used), and a minimum 7-day re-application interval. The re-entry interval for both products is 12-hours and a 3-day preharvest interval must be observed for both. This compound is highly toxic to bees and remains toxic to bees exposed to residues for more than 38 hours following an application. This Section 18 for use of dinotefuran in Virginia pome and stone fruit will expire on October 15, 2020.
CM and OFM Degree Days and Optimal Spray Timing, 7.16.20
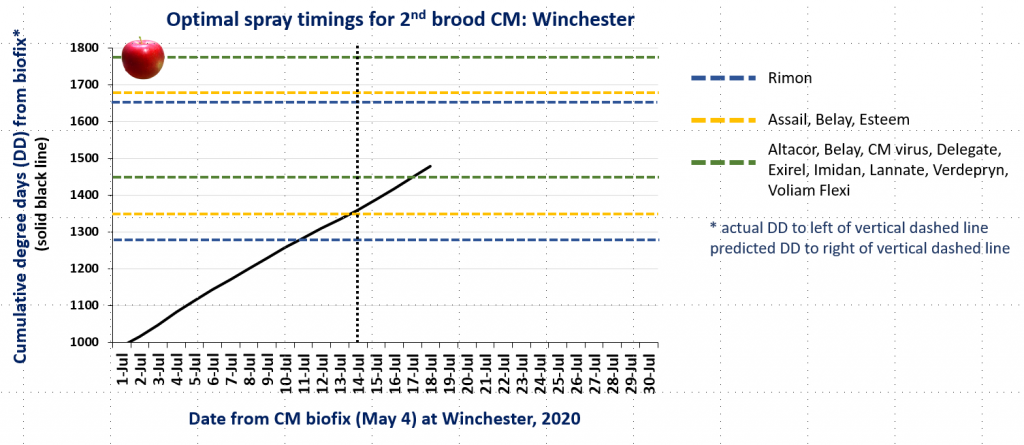
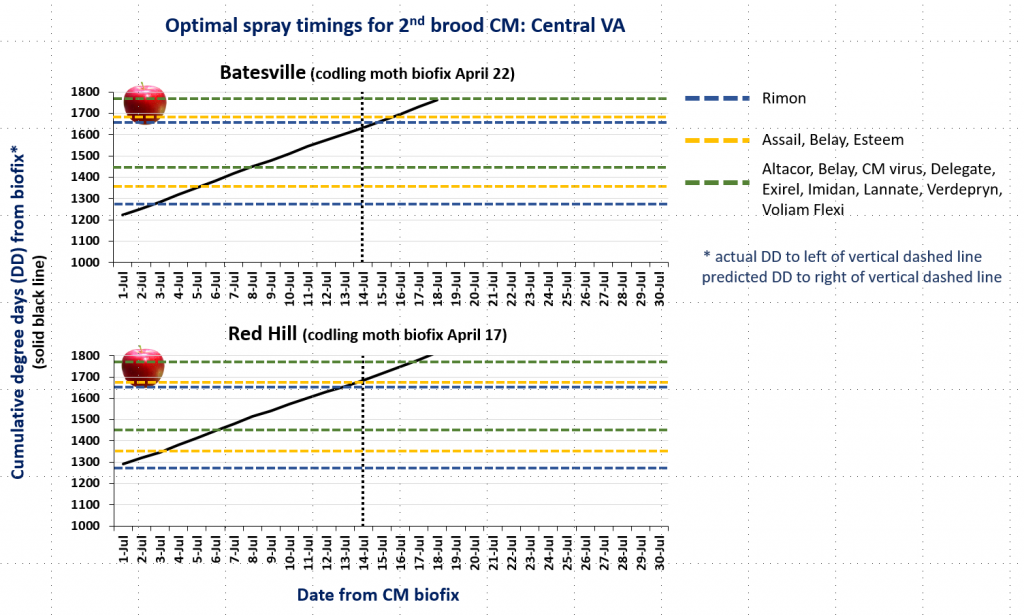
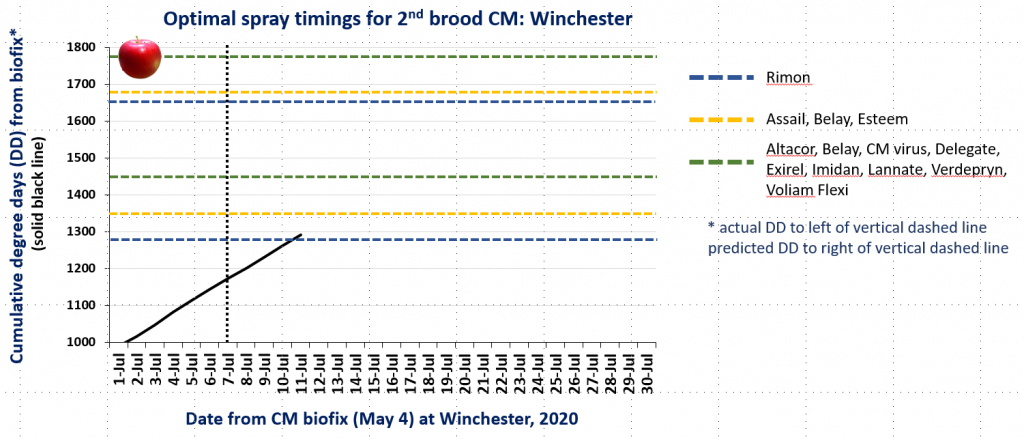
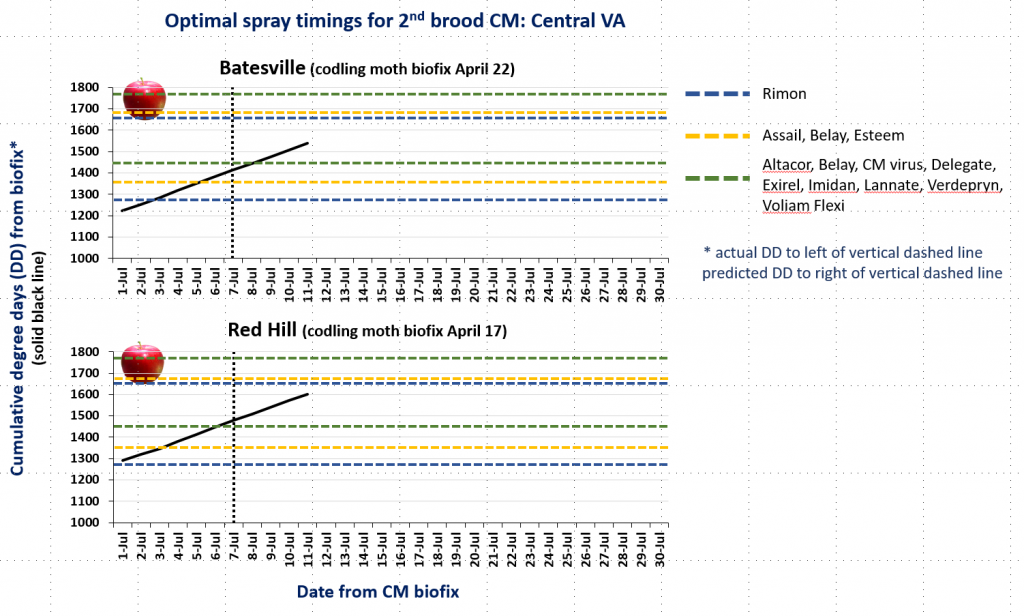
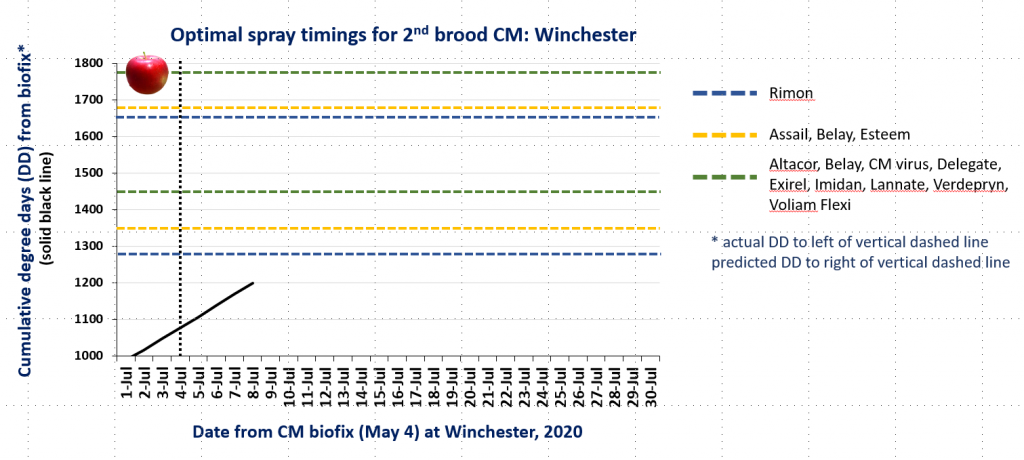
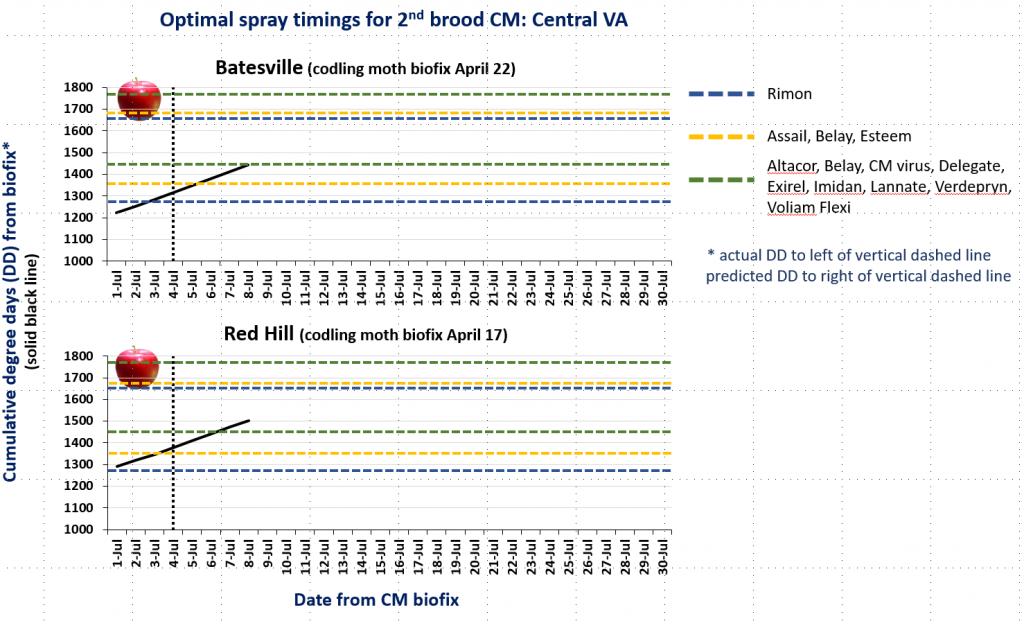
In the attached graphs for CM degree day accumulation in central Virginia you will note that the last optimal timing for managing 2nd brood CM larvae using products indicated by the green lines is within the next 1-3 days, based on model predictions using a biofix of April 17 and 22 for the Red Hill and Batesville areas, respectively. After 2nd brood, the model is not used, so management decisions can be based on whether or not CM captures in pheromone traps exceed the threshold of an average of 5 moths/trap/week.
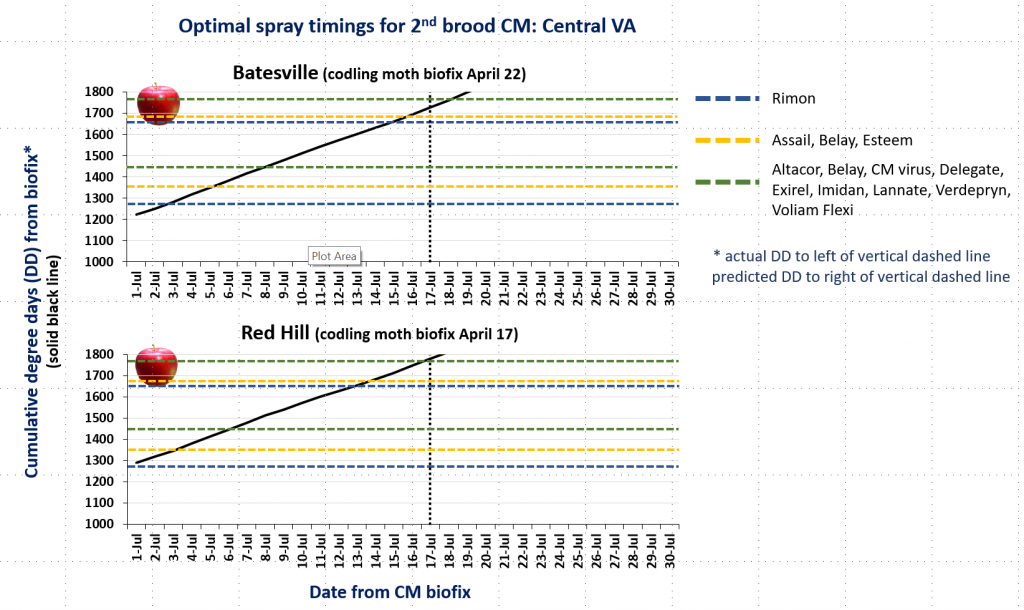
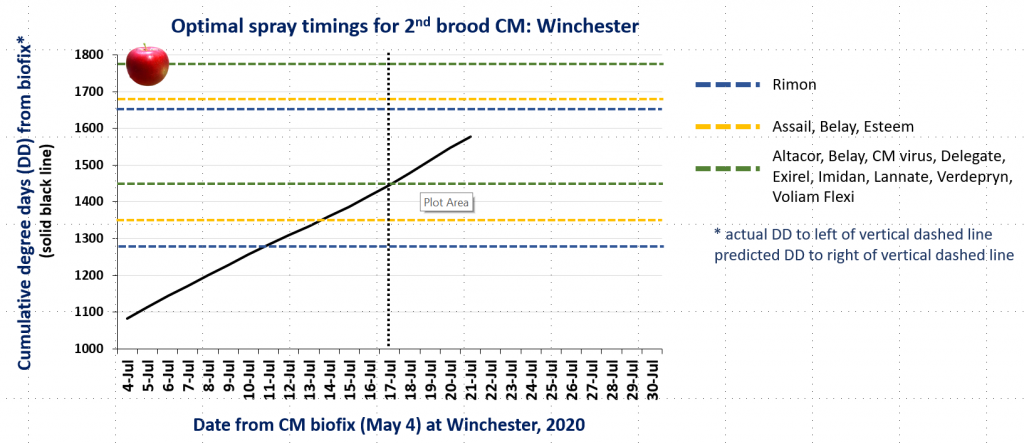
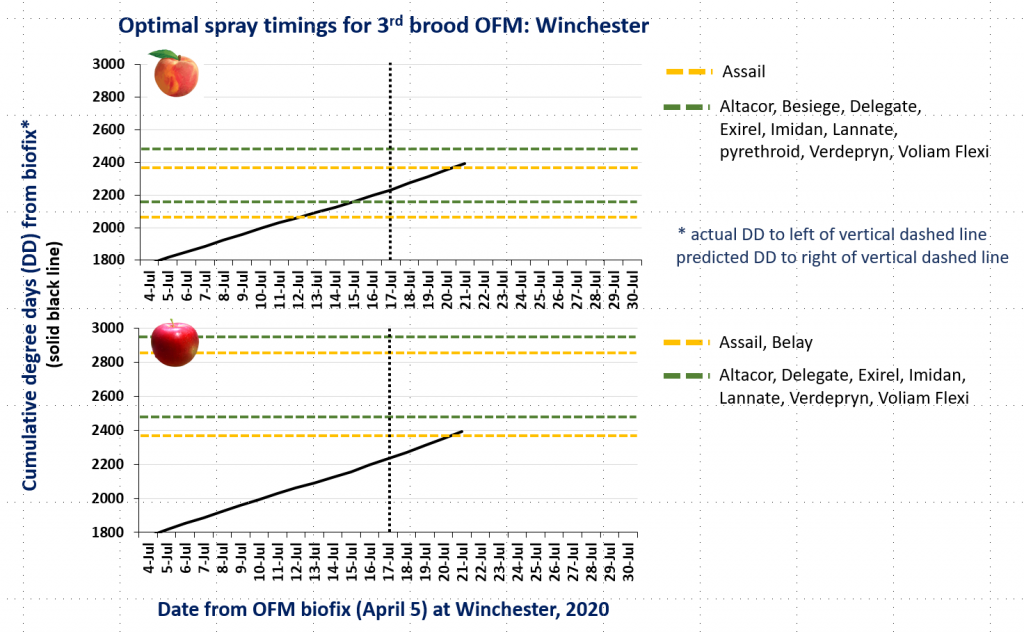
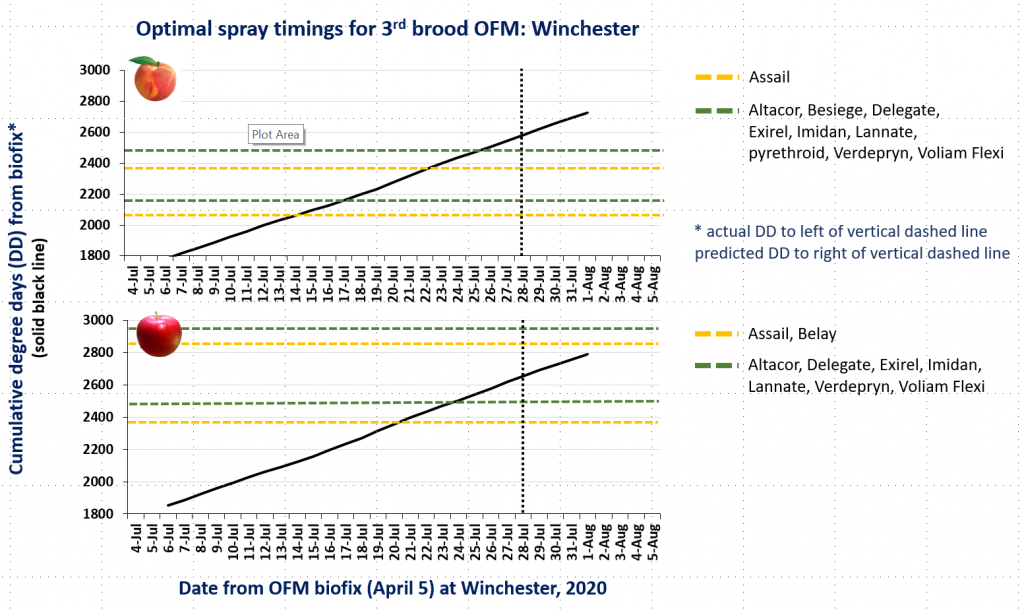
CM and OFM Degree Days and Optimal Spray Timing, 7.13.20
CM and OFM Degree Days and Optimal Spray Timing, 7.9.20
You may have noticed in my previous posts regarding degree days and optimal timings that some of the chemical names shown to the right of the graphs were underlined in red and others were not. This was an oversight of mine that Keith Yoder pointed out to me today. It was due to my not having these names in my “dictionary” and did not indicate any recommendation of one product versus another. Note that this has been corrected.
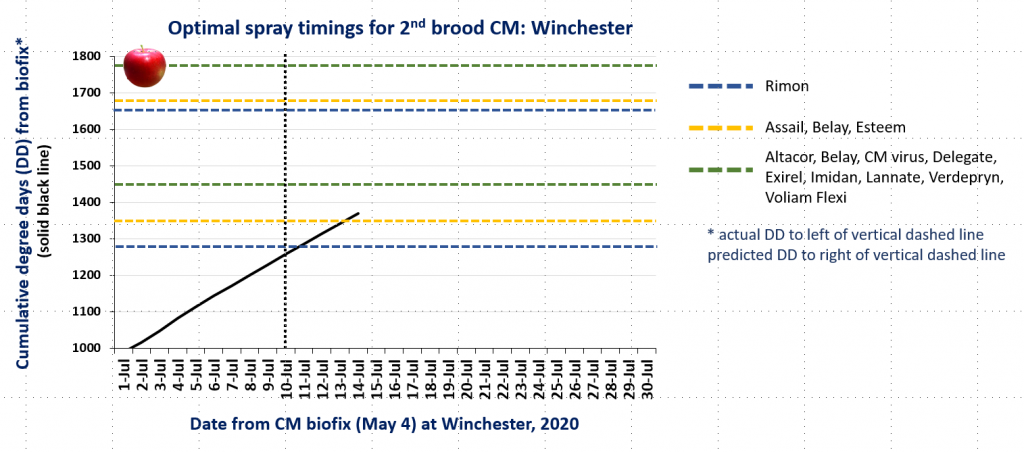
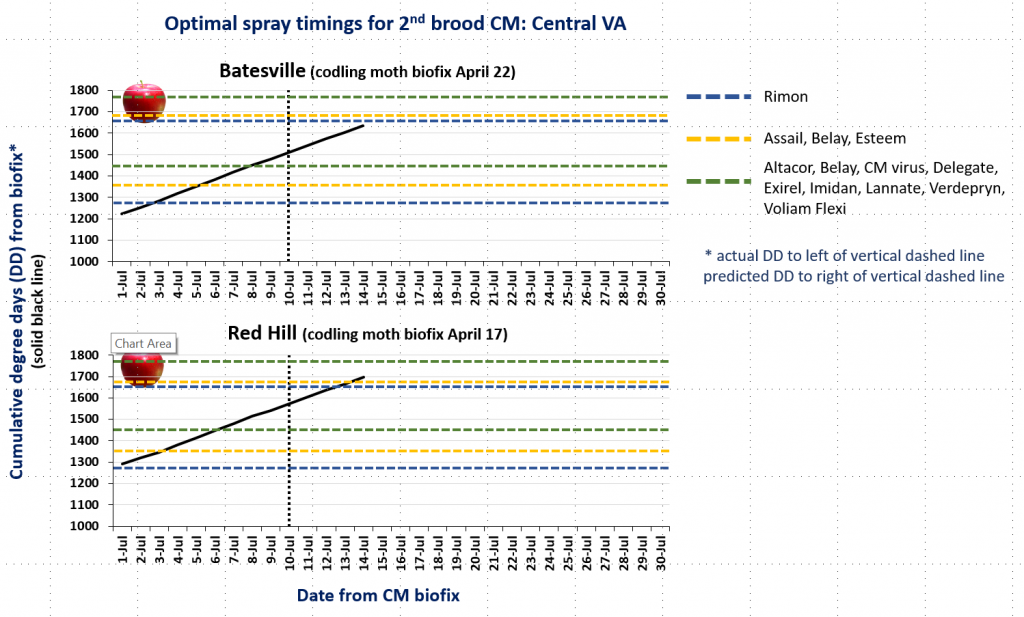
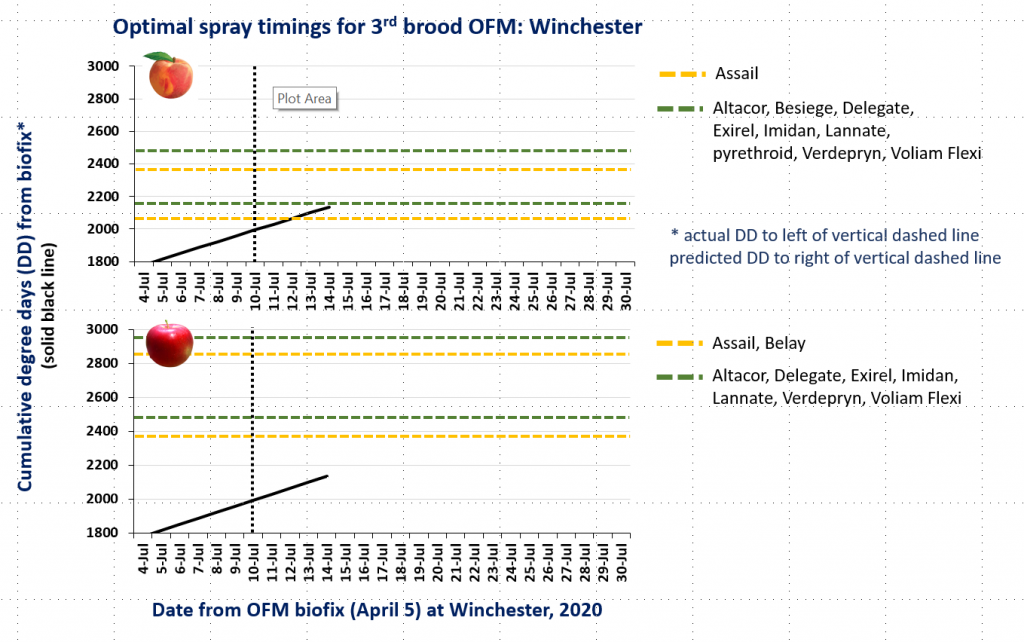
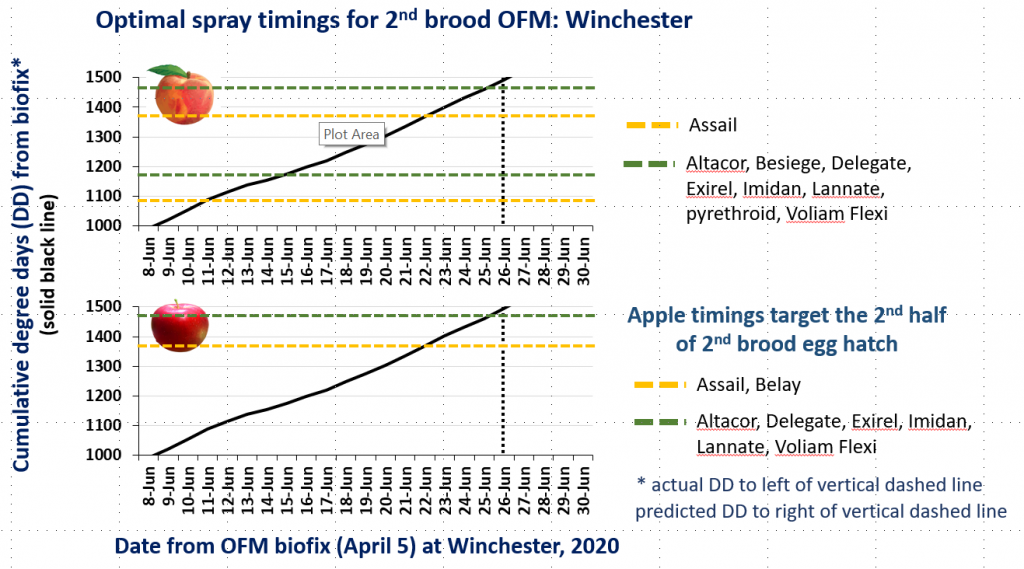
CM and OFM Degree Days and Optimal Spray Timing, 7.6.20
CM Degree Days and Optimal Spray Timing, 7.3.20
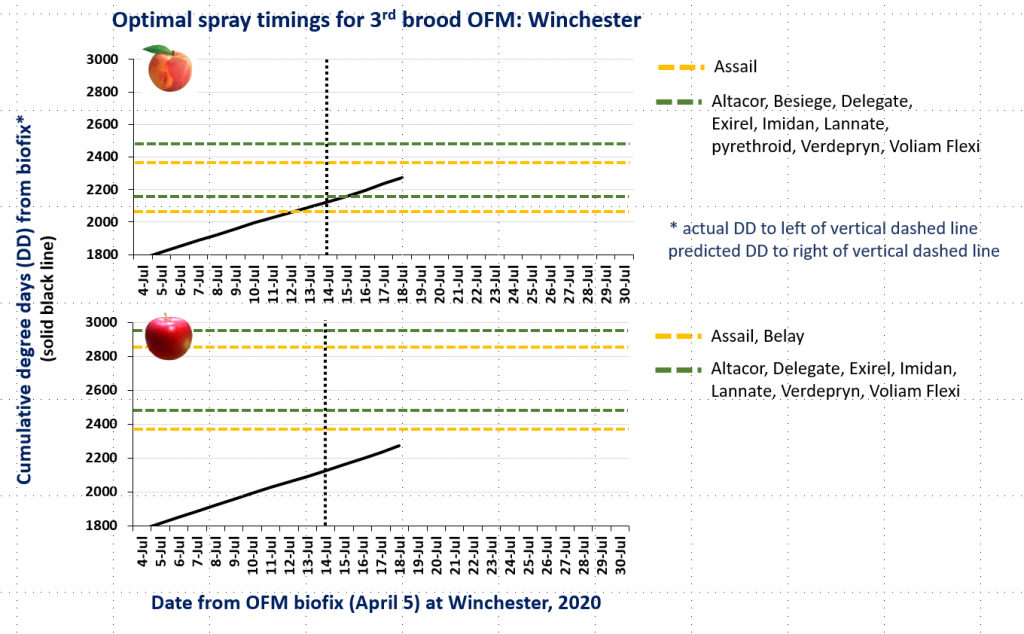
OFM Degree Days and Optimal Spray Timing, 6.25.20
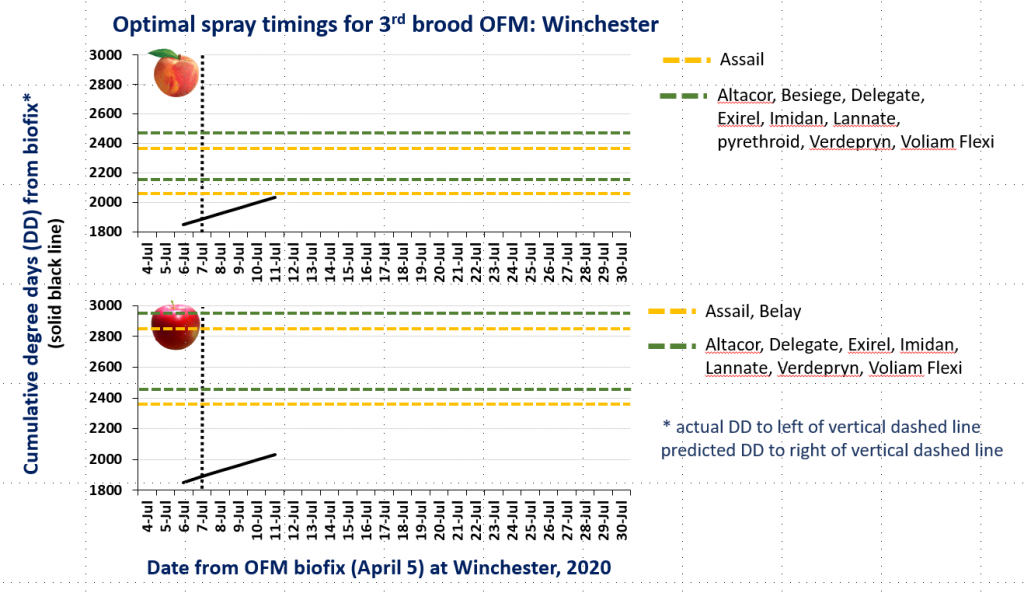
As of June 25, the degree day model for predicting hatch of 1st brood codling moth eggs shows 97% hatch for Winchester and 100% hatch for Batesville and Red Hill in central Virginia. Recent research by Dr. Jim Walgenbach from North Carolina showed that the traditional codling moth developmental model from Michigan State was predicting an earlier flight of second generation adults in our region than was reflected by pheromone traps. Therefore, recommendations for timing sprays against 2nd brood codling moth larvae were revised by adding 200 degree days to the timings recommended by the Michigan model, and this has proved to perform well. I will resume posting codling moth degree day accumulations for our area as we get nearer to the critical timings for 2nd brood. Similarly, I will resume posting degree days for oriental fruit moth when we approach those critical timings for 3rd brood.