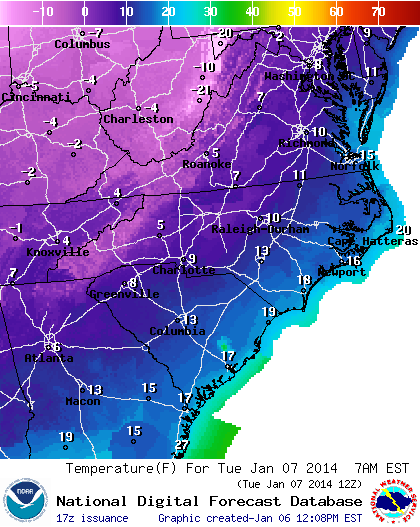
This week and weekend, the temperature is expected to drop below freezing, and some areas throughout the state may even experience snow showers. While the apples, cherries, and peaches in our location in Winchester, VA aren’t at great risk yet because the flowering buds are not yet at a developmental stage that raises red flags, other parts of the state, particularly around central and southwestern Virginia, could be at a much more advanced stage, particularly for stone fruits. These freezing temperatures might be a cause for concern.
That’s why some growers might be thinking about using irrigation sprinklers for frost protection. It’s a convenient method if you already have them in your orchard. But, I’ve noticed over the years that some might be using sprinklers the wrong way or when they’re not necessary, which can cause more harm than good.
I hope we don’t experience any damaging frost this season, but if we do, and you’re considering turning on your sprinklers as your last resort in the face of spring frost, I’ve recycled some information from old blog posts to remind you of the science and application of using sprinklers for frost mitigation. So, here’s a quick read to help you understand how to use sprinklers effectively and safely.
If you’re looking for a way to protect your trees from frost damage, using sprinklers (e.g. overhead or under-tree irrigation sprinklers) may be a viable solution. When you use sprinklers, you are essentially harnessing the latent energy of water molecules as a source of heat to warm up your trees. But how does this work exactly?
To understand this phenomenon, it’s important to note that water exists in three states: liquid, solid (ice), and gas (vapor). The transition among these states can either produce energy (exothermic) or consume energy (endothermic).
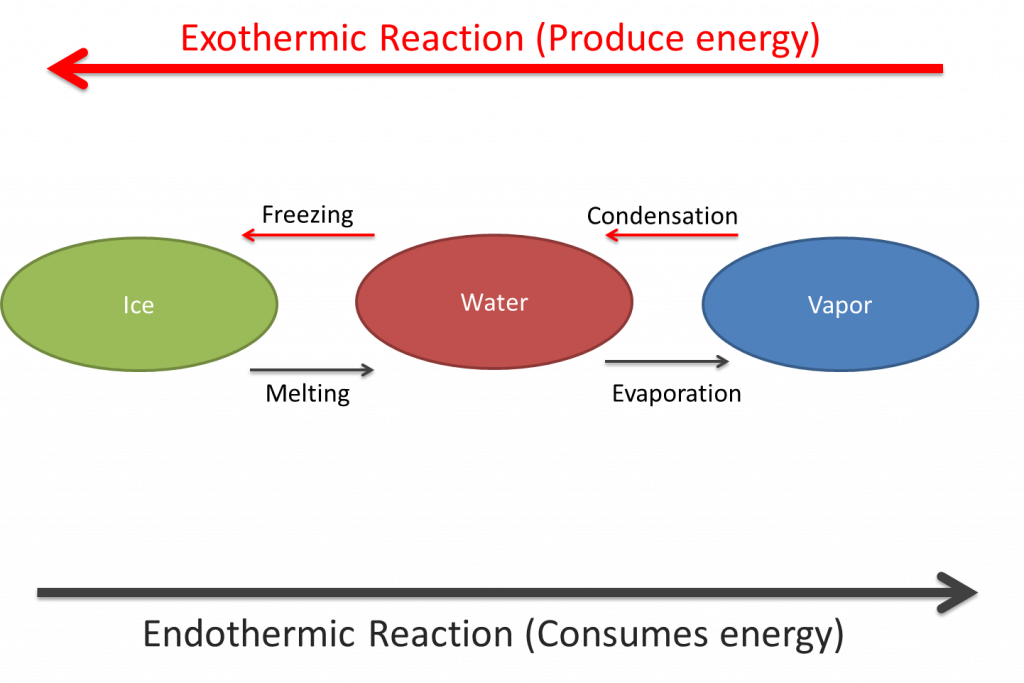
When the air temperature drops below freezing point (< 32°F), and you use sprinklers, you encourage the transition of water from its liquid phase into ice. This process releases latent energy into sensible energy (heat) that plant tissues can use to warm up.
While this may seem like an ingenious solution, there are some potential drawbacks to using sprinklers. To ensure that using sprinklers to reduce frost damage doesn’t harm your plants, there are three crucial things to consider. Let’s take a closer look at each one.
First and foremost, it’s essential to keep an eye on the wind. This is because wind can encourage the transition of water from its liquid phase into its gaseous phase (vapor). During this process, heat in the air and around your plants will be consumed in an endothermic reaction. That’s why it’s recommended that you avoid using sprinklers if the wind speed is above 10 mph.
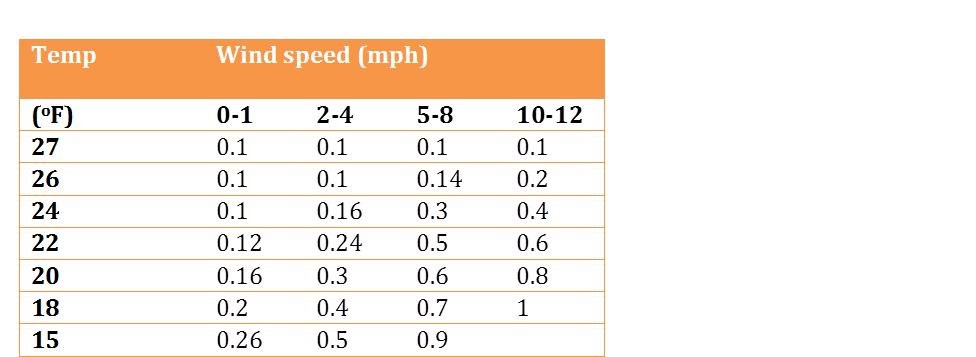
To help you determine the amount of water needed under different wind conditions and temperatures, refer to the table below (Table 1).
Table 1 provides information on the amount of water (in inches per hour) that should be provided for frost protection under different wind speeds (in miles per hour). This table is based on information from the University of Florida Extension Circular 287.
The second thing you need to consider when using sprinklers to reduce frost damage is the dew point. In simple terms, low dew points mean low humidity. If the dew point is too low, the water you add through sprinklers will quickly evaporate to compensate for the low humidity. This will cool down the air around your plants, which will cause more damage.
Under moderate dew points, a portion of the water you add through sprinklers will turn into vapor and consume heat, while another part will turn into ice and produce heat. After some time, the net energy will be positive, and you’ll reap the benefits of using sprinklers. However, if the dew point is too low, it means that the air is too dry and will take much longer to become saturated with vapor. During this time, the air temperature may drop to a critical temperature that can damage your buds or flowers. In this scenario, using sprinklers may cause more harm than good to your plants.
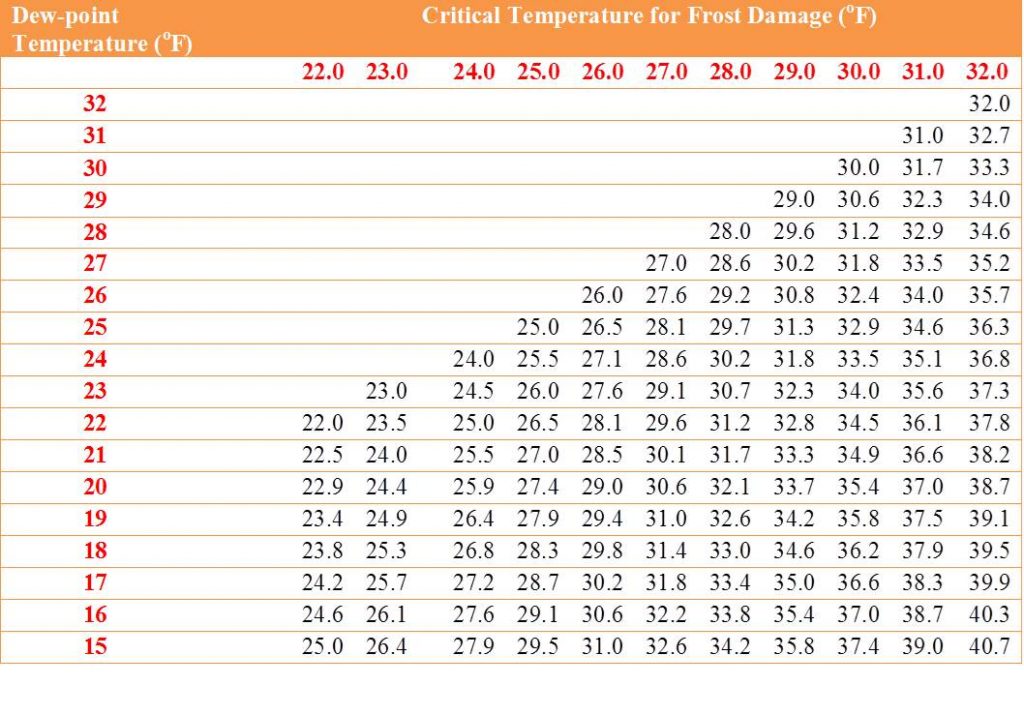
To help you determine whether sprinklers will be useful in your situation or not, refer to the table below (Table 2) to determine the temperature at which you should turn your sprinklers on/off. If the dew point and the critical damage temperatures are not within the range shown in the table, it’s best to avoid using sprinklers altogether.
Table 2 provides information on the minimum temperature at which sprinklers should be turned on/off. This data comes from UC-Davis and is part of their FP005 Quick Answers guide.
To determine when to turn your sprinklers on and off for frost protection, use a critical temperature for frost damage (columns) and dew-point temperature (rows) chart. The point where the row and column intersect is the temperature at which you should turn on or off your sprinklers. It is generally recommended to use sprinklers to protect against temperatures in the range of 24 to 32F.
To find out the critical temperature at which 90% of the flower buds can be killed, please refer to the following link: https://blogs.ext.vt.edu/tree-fruit-horticulture/2022/03/27/hard-freeze-is-expected-this-tuesday-march-29/
You can get the dew point information for your location by using your zip code on Intellicast at http://www.intellicast.com/Local/Weather.aspx?location=USVA0837.
The third factor to consider is the amount of water your sprinklers can provide. If you’re uncertain whether your sprinklers can provide an adequate amount of water, it’s best not to use them at all. Refer to Table 1 to determine the amount of water required under different conditions.
By considering these three factors, you can ensure that using sprinklers to reduce frost damage is effective and safe for your trees.


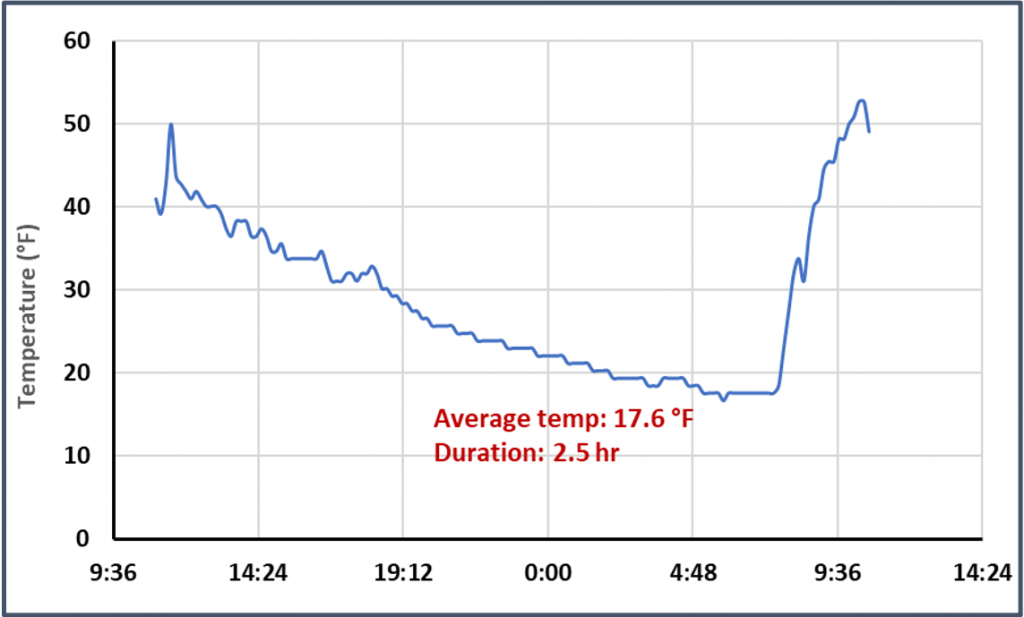
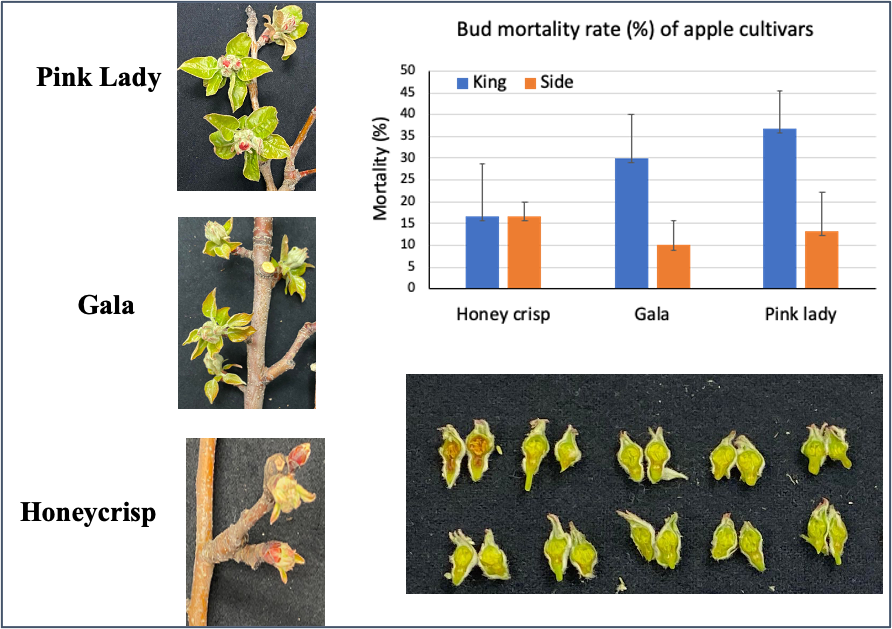


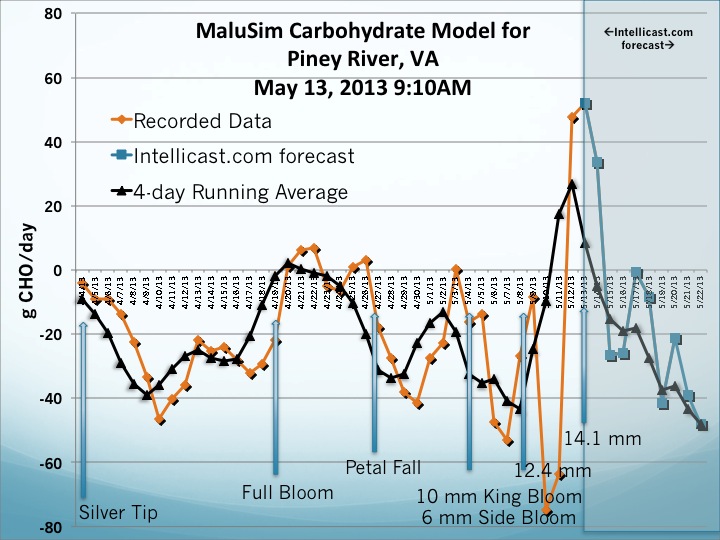
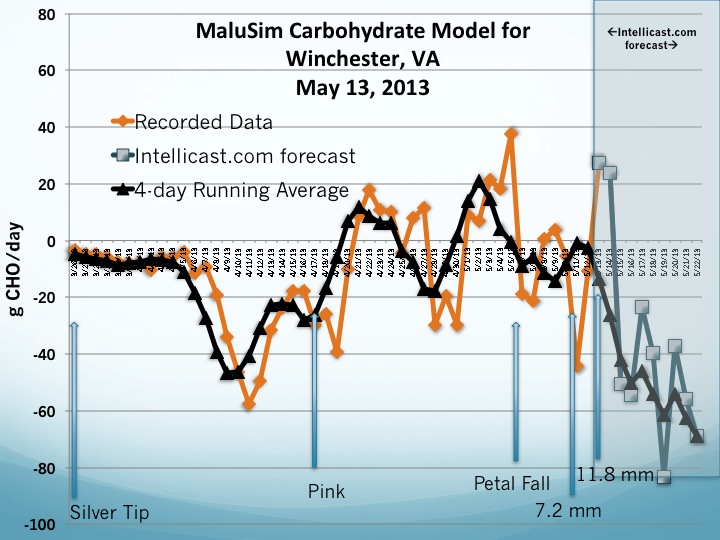 The MaluSim carbohydrate model was run on May 13 for both Winchester and Central Virginia.
The MaluSim carbohydrate model was run on May 13 for both Winchester and Central Virginia.

