Charlie Cahoon, Extension Weed Specialist
Eastern Shore AREC-Virginia Tech
Italian ryegrass is one of the most common and troublesome weeds Virginia small grain producers face. The weed competes with wheat for essential nutrients, sunlight, and moisture and also interferes with harvest. In the past, growers have relied upon herbicides, such as Axial XL, Hoelon, PowerFlex, and Osprey, for control of Italian ryegrass. However, herbicide resistant Italian ryegrass biotypes have developed, limiting the herbicide options available to growers.
During the summer of 2016, the weed group at the Eastern Shore AREC traveled Eastern Virginia in search of resistant Italian ryegrass. To broaden the survey, we solicited samples from extension agents and members of the agriculture industry. In total, 82 samples were collected throughout Eastern Virginia (Image 1). The objective of this survey (and subsequent resistance screening) was to determine the distribution of resistant biotypes in Virginia; allowing growers to tailor management strategies specific to biotypes in their area.
Italian ryegrass heads collected during the summer were allowed to dry down and then threshed to separate the seed. Approximately 400 seed from each population were planted in a seed tray. Once Italian ryegrass reached 3.5 to 4 inches in height (1 to 2 leaf), plants were treated with a 1X rate of Axial XL (16.4 oz/A), Hoelon (43 oz/A), PowerFlex HL (2 oz/A), and Osprey (4.75 oz/A). A non-treated check from each sample location was included for comparison purposes. Visual injury was recorded at 28 days after treatment (DAT) for Italian ryegrass treated with Axial XL and Hoelon. PowerFlex HL and Osprey are both ALS-inhibiting herbicides and act much slower than the ACCase-inhibiting herbicides (Axial XL and Hoelon). Therefore, ryegrass treated with these products were evaluated 42 DAT. Also at 42 DAT, Italian ryegrass biomass (and subsequent % biomass reduction) was determined by cutting and weighing the above ground portion of ryegrass.
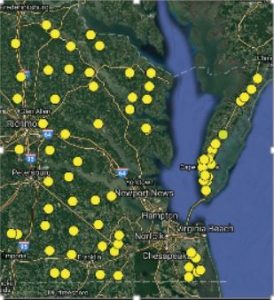
Image 1. Locations of 2016 Italian ryegrass samples collected.
Overall, approximately 23% of all samples collected were resistant to Axial XL (Image 2) compared to 30% that were resistant to Hoelon (data not shown). Most samples resistant to Hoelon were also resistant to Axial XL. However, for 6 samples, Axial XL remained effective despite poor Hoelon activity. Axial-resistant Italian ryegrass is widespread in two of Virginia’s major wheat producing regions (Eastern Shore and southern Chesapeake/Virginia Beach). Of the 14 samples collected in Northampton Co., 9 were found to be resistant to Axial XL (64%). In contrast, none of the 5 samples collected from Accomack Co. were Axial-resistant. In southern Virginia Beach and Chesapeake, 5 of 6 samples collected were resistant to Axial (83% of samples). Excluding the Eastern Shore and southern Chesapeake/Virginia Beach, only 9% of remaining samples were resistant to Axial XL; 1 samples east of Stony Creek in Sussex Co.; 1 sample south of Waterview in Middlesex Co.; 1 sample northeast of Newtown in King and Queen Co.; 1 sample northwest of Loretto in Essex Co.; and 1 sample south of Somers in Lancaster Co.
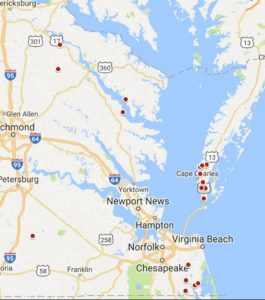
Image 2. Distribution of Axial-resistant Italian ryegrass in Virginia.
ALS-resistant Italian ryegrass is more widespread throughout eastern Virginia. Of the surveyed populations, 92 and 93% were resistant to Osprey and PowerFlex HL, respectively. Producers should keep in mind the presence of herbicide-resistant Italian ryegrass nearby does not automatically mean they have a resistant biotype on their farm. Fields with escaped Italian ryegrass were purposely chosen for this survey. It is best to rely on field history and performance of herbicides in the past when making management decisions. However, it is always a good idea to rotate modes of action to delay the development of resistant biotypes.
Unfortunately, if ryegrass is resistant to Axial XL and the ALS-inhibiting herbicides (Osprey and PowerFlex HL), there are no postemergence options left. In this situation, a residual product that includes pyroxasulfone (Anthem Flex and Zidua) is suggested delayed-preemergence or early postemergence. These products offer residual control of ryegrass only (they will NOT control emerged ryegrass). It is imperative that these products are applied and activated by a timely rainfall prior to ryegrass emergence. Rotating away from wheat also presents an opportunity to control Italian ryegrass (and prevent seed production) with glyphosate early burndown prior to planting corn or full-season soybean. Be aware that glyphosate-resistant Italian ryegrass is suspected in northeast North Carolina and eastern Virginia. In this situation, paraquat plus a residual herbicide like s-metolachlor applied to fallow ground during the fall would be in order.

Image 3. Axial XL-susceptible Italian ryegrass collected near Nassawadox, VA treated with no herbicide (left), Axial XL at 16.4 fl oz/acre (middle), and Hoelon at 43 fl oz/acre (right).

Image 4. Axial XL-resistant Italian ryegrass collected near Cheriton, VA treated with no herbicide (left), Axial XL at 16.4 fl oz/acre (middle), and Hoelon at 43 fl oz/acre (right).