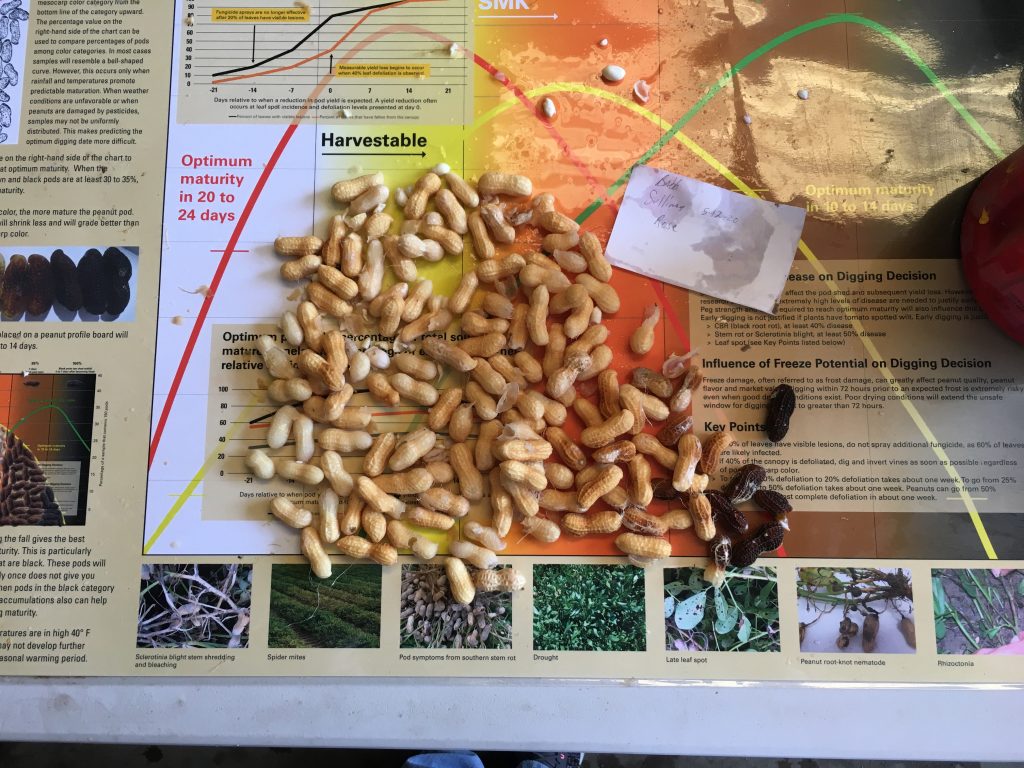
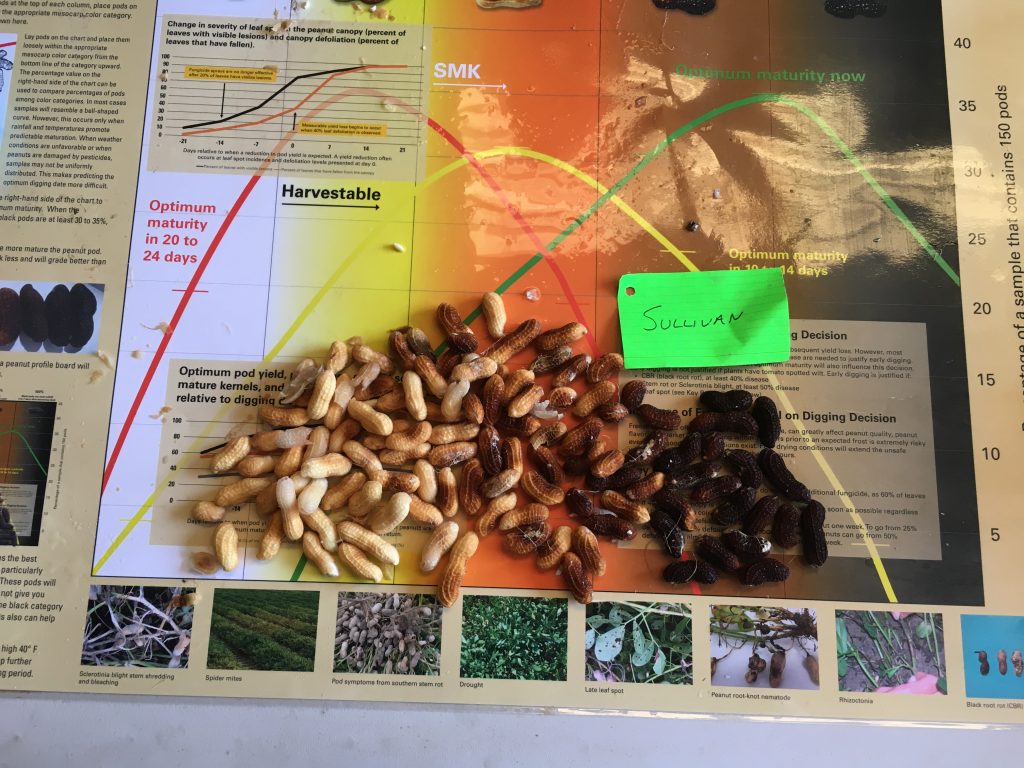
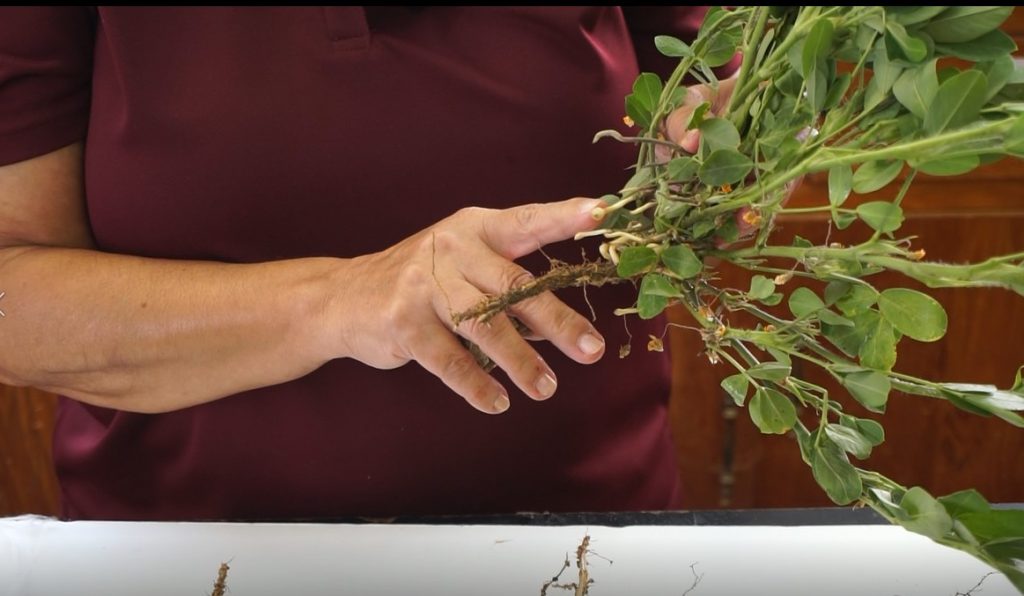
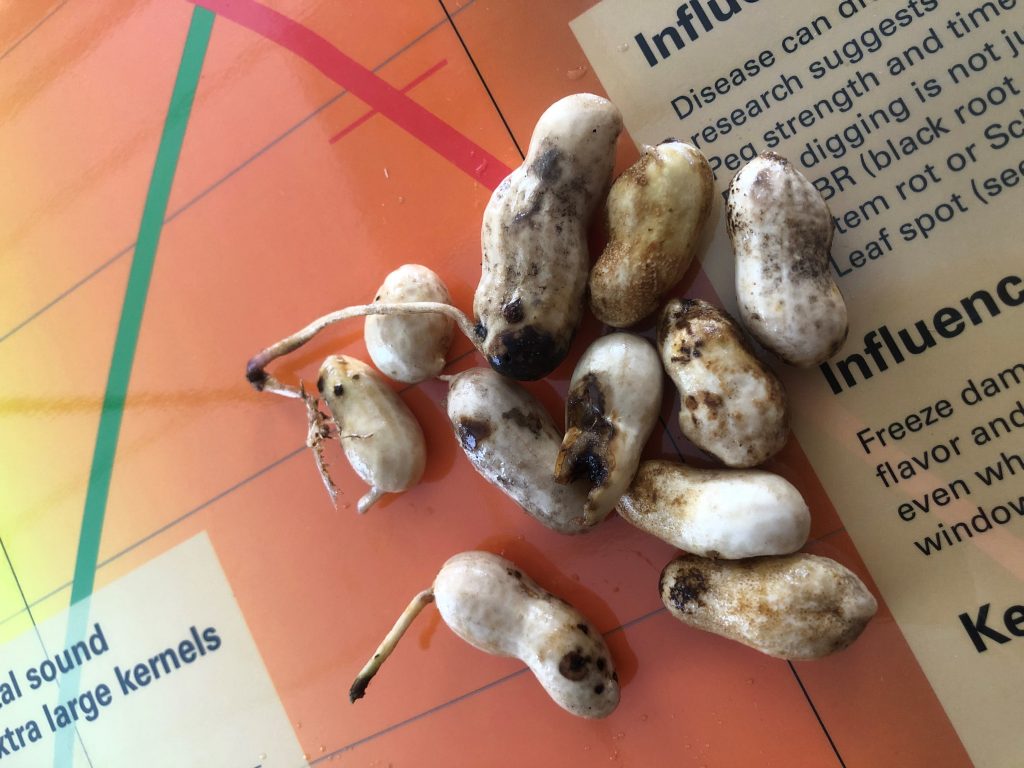
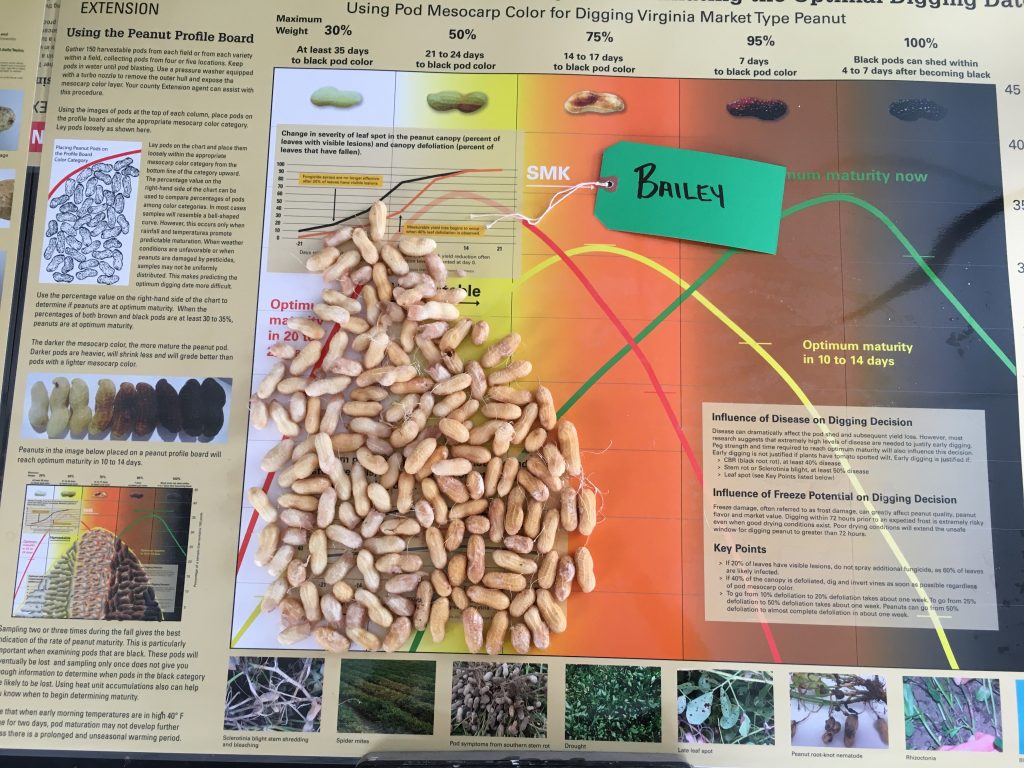
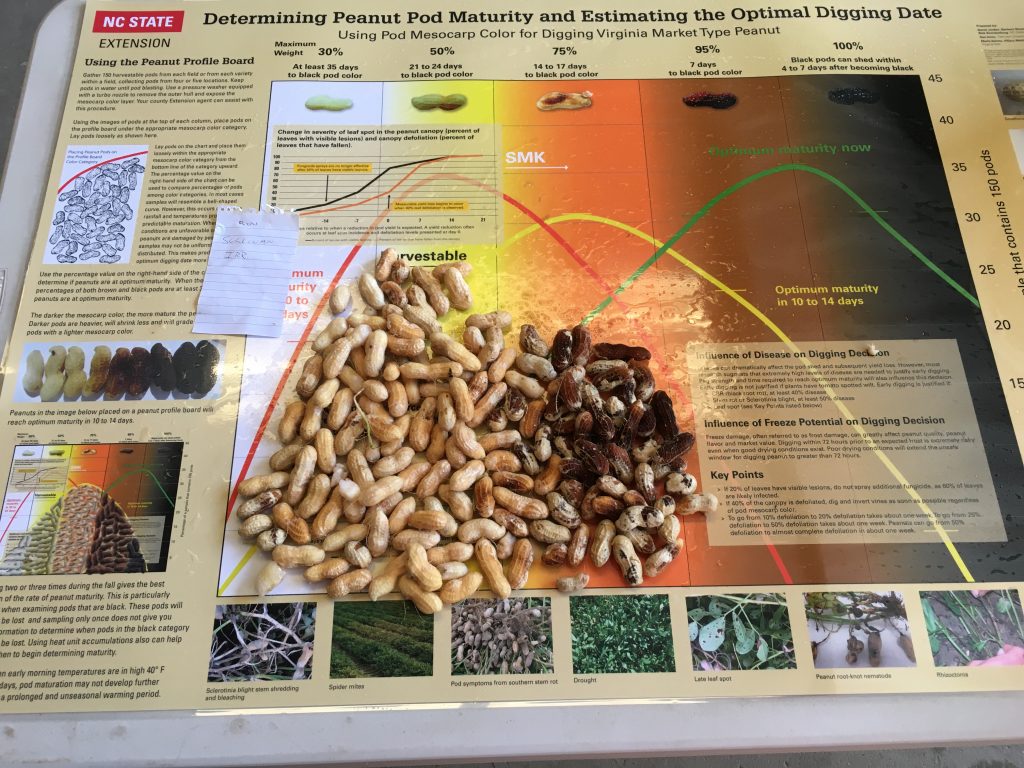
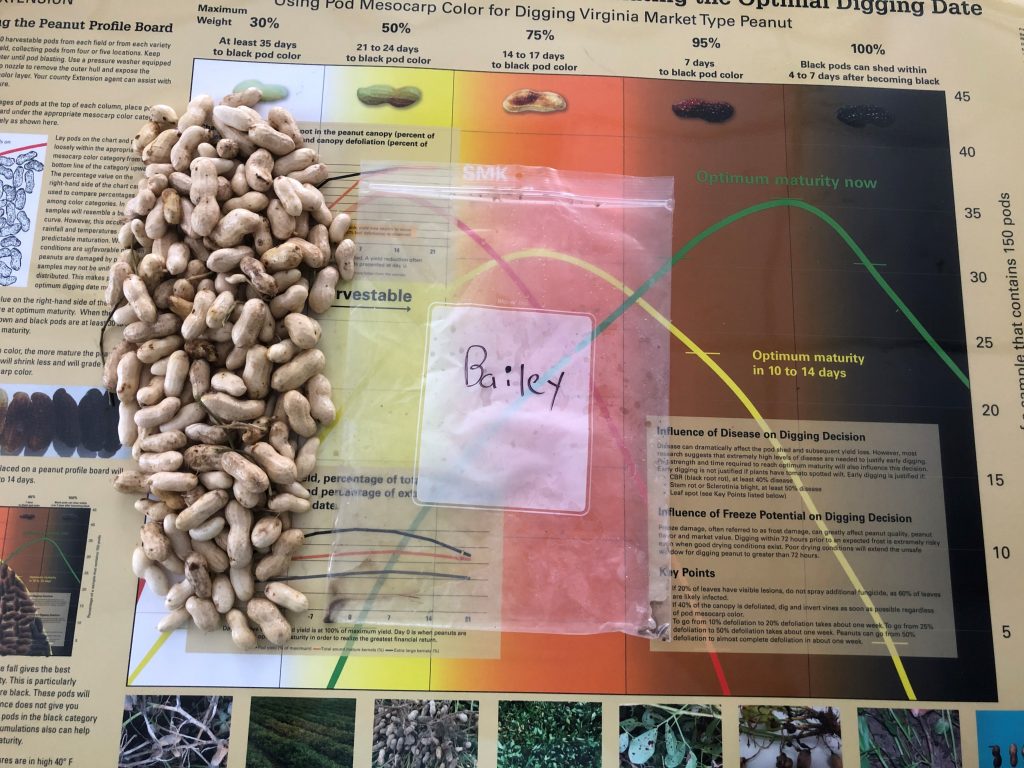
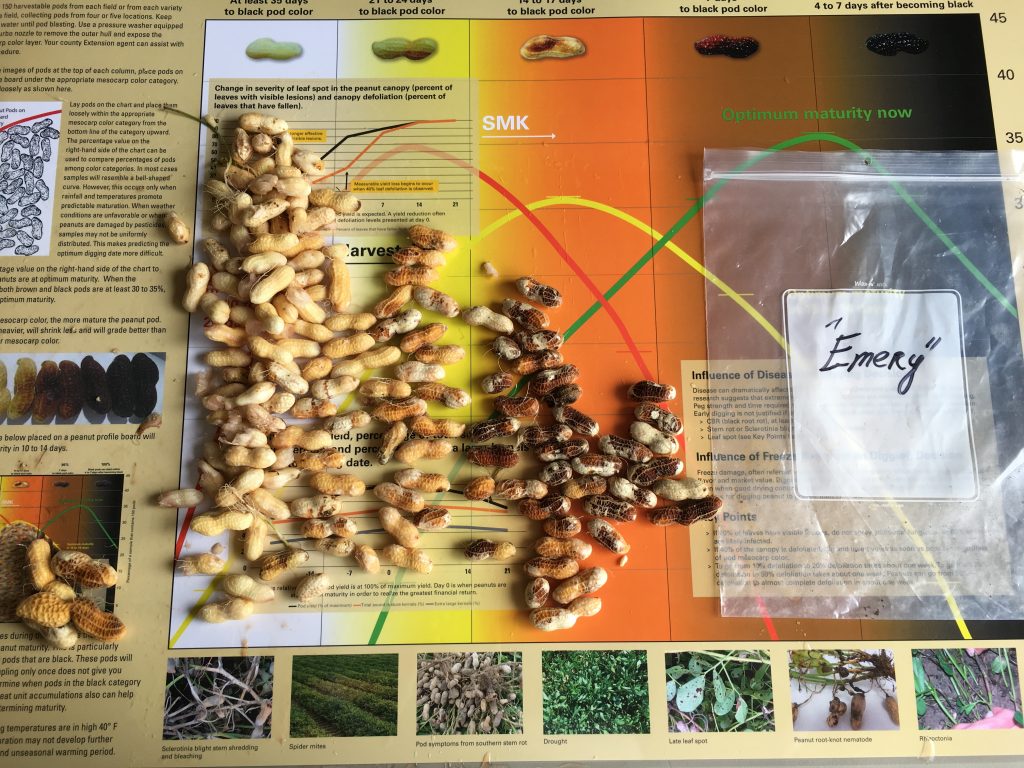
Frank Bryant pod blasting the peanut pods (left) and growers commenting on the pod samples (right).
Monday, Sep 14 2020, Extension Agent Livvy Preisser organized a pod blasting clinic in Windsor, VA, at the Indika Farms Inc.
As every year my technician, Frank
Bryant, assisted the Agent with this activity. Keeping the distance, several
growers brought over 25 peanut samples from almost 2000 acres from the
neighboring fields.
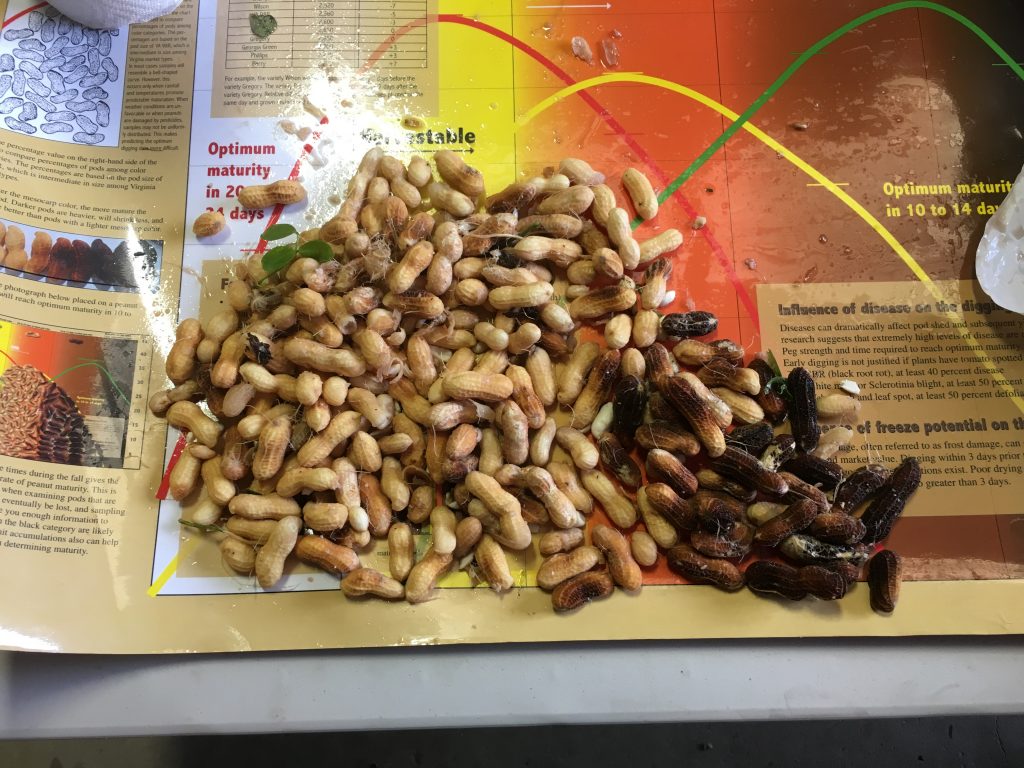
In average, peanut still needs 3
weeks or longer to complete physiological maturity, regardless if the fields
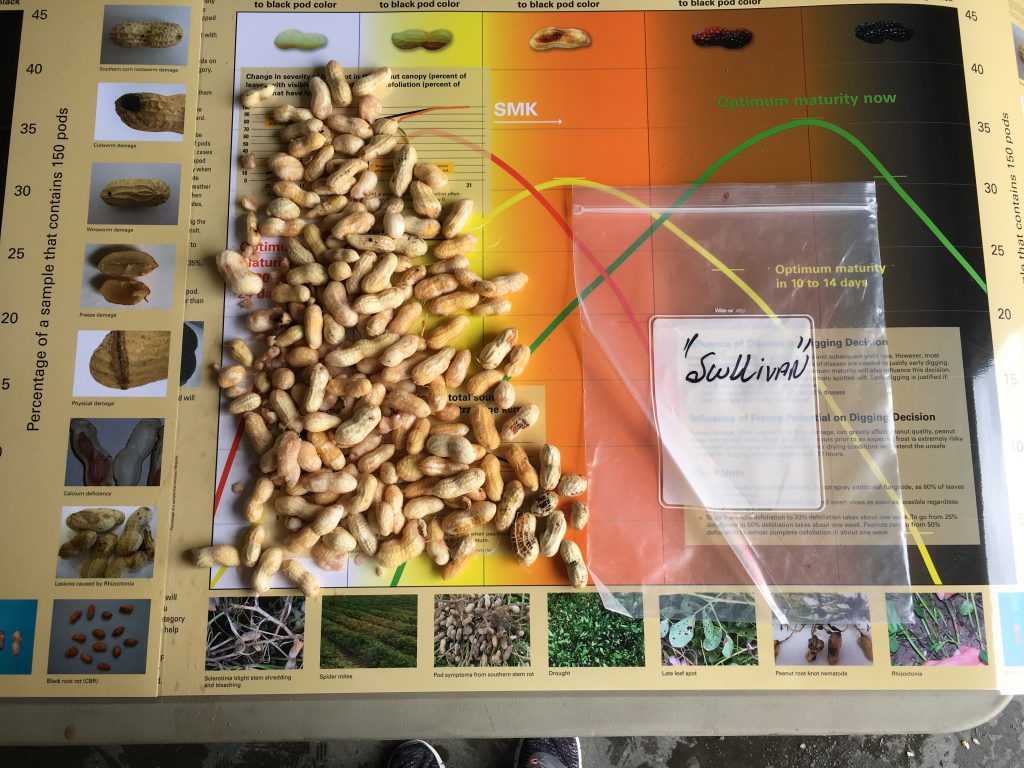
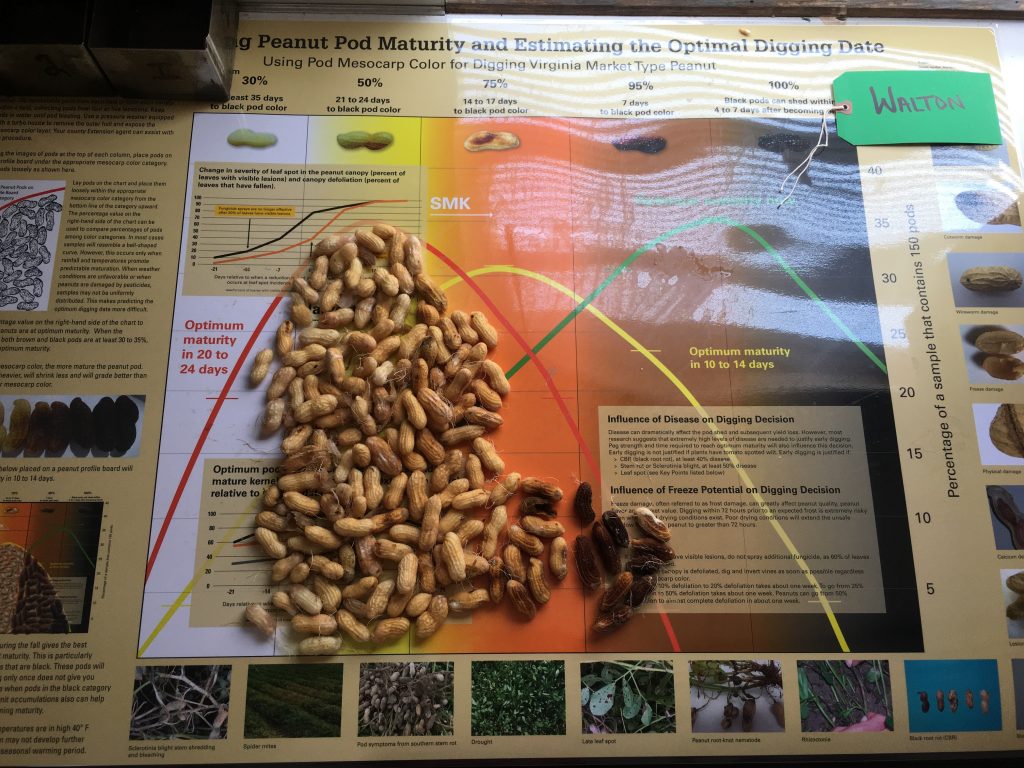
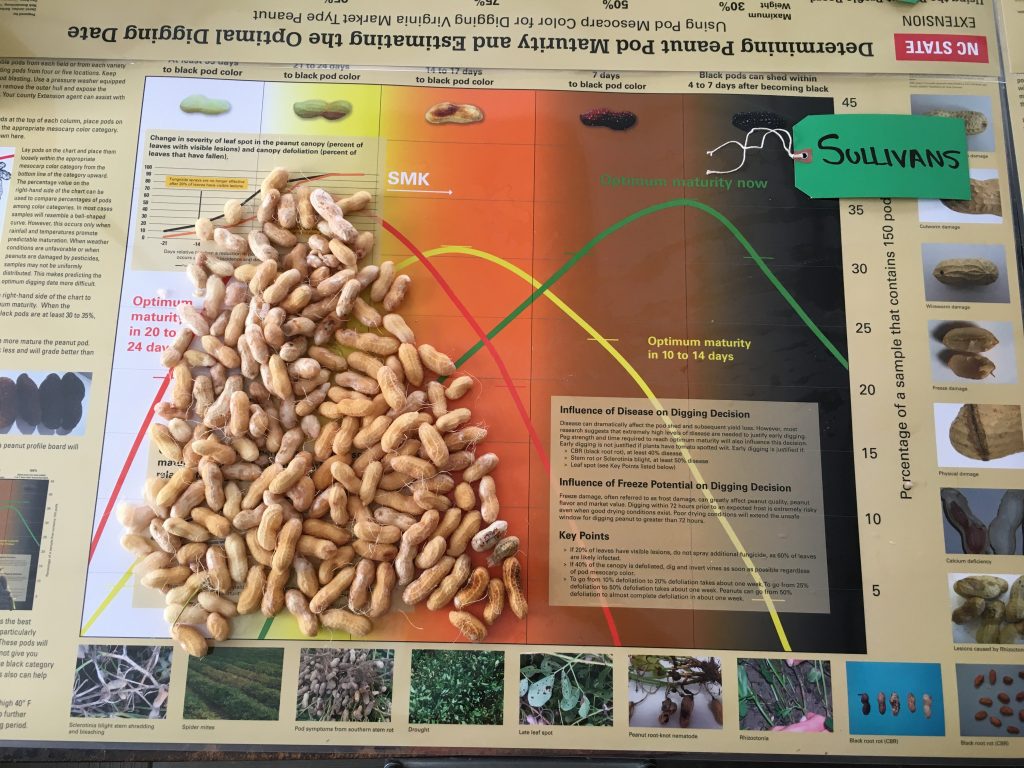
were or not irrigated. From all, only one sample of non-irrigated Sullivan was
2 weeks closer to digging. This agrees
with what we have observed in the research plots this week.
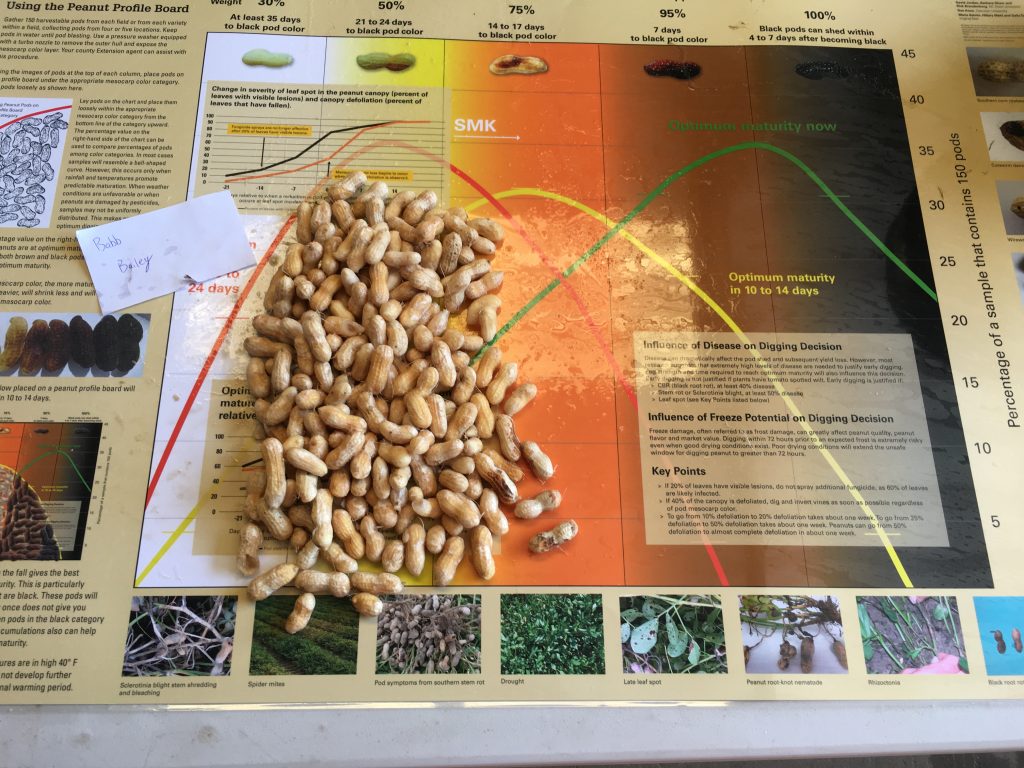
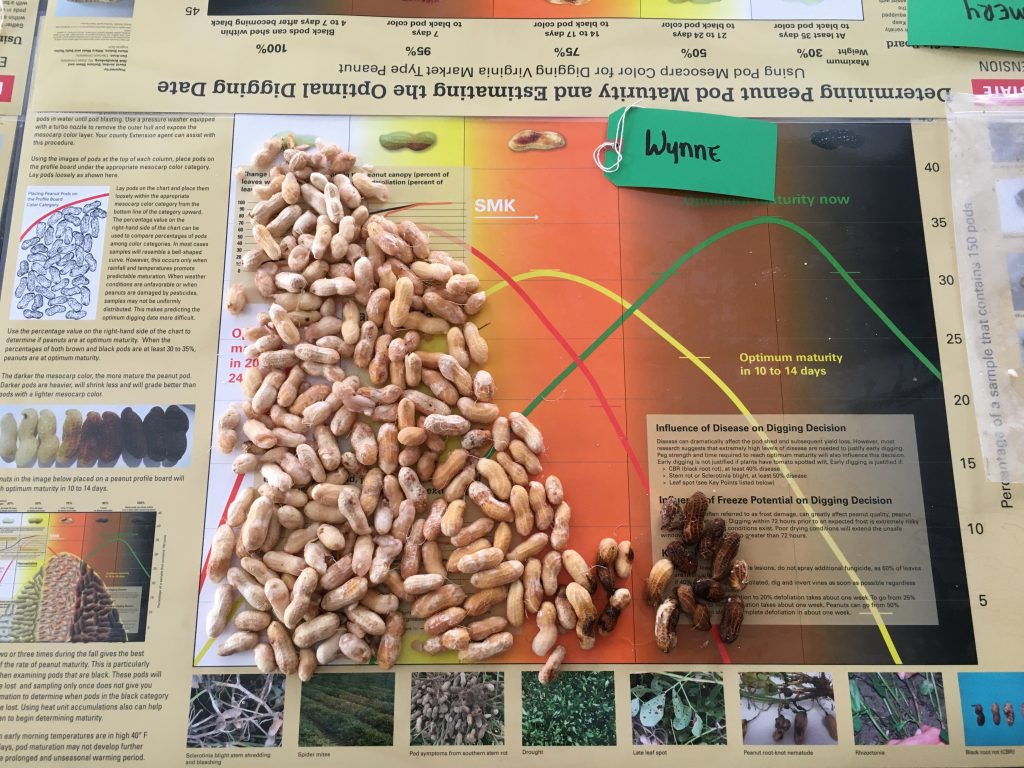
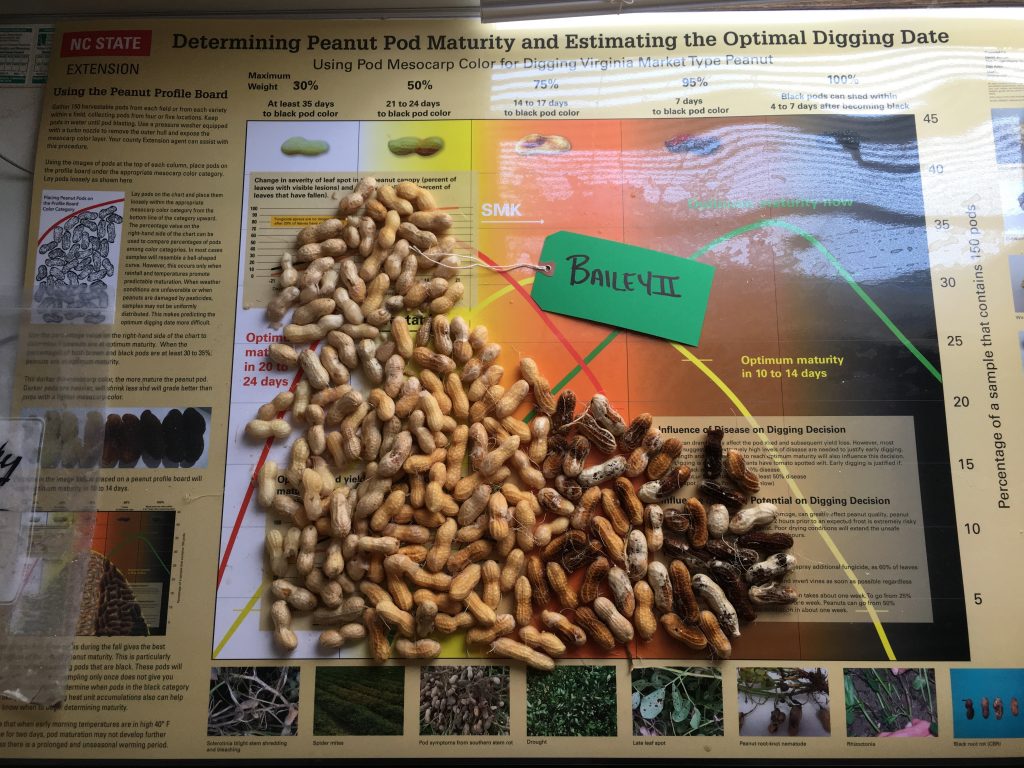
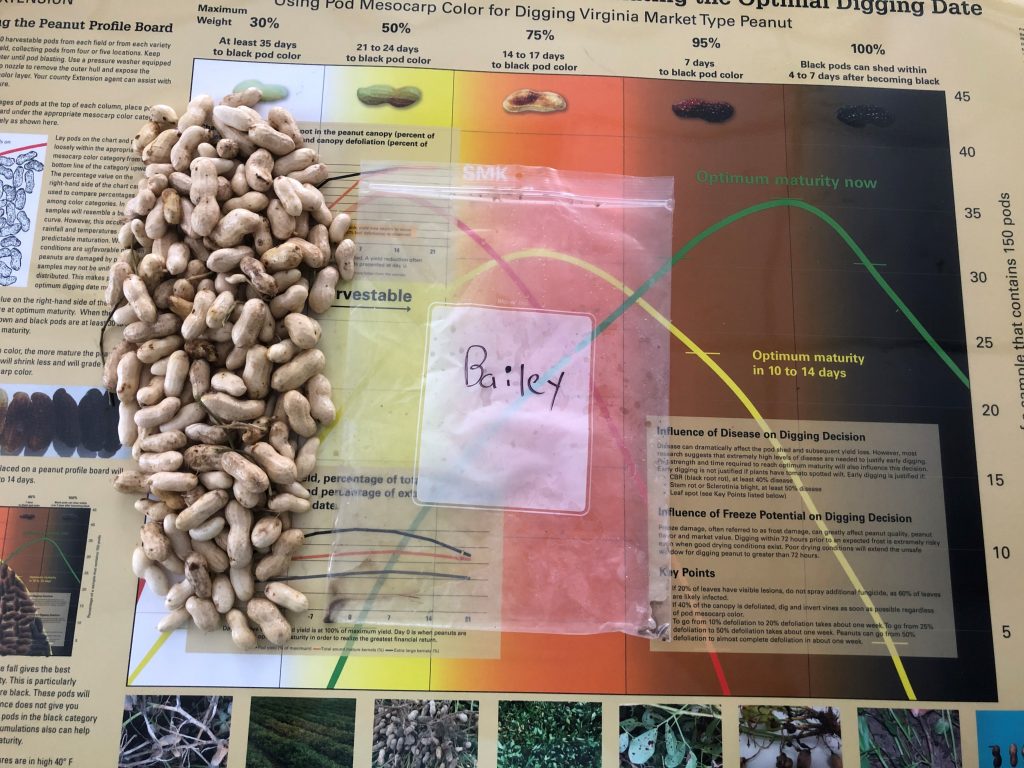
Maturity of peanut in Isle of Wight County, VA, on Sep 14, 2020. Samples are from different fields, Bailey (upper left and center), Bailey II (upper right), and Sullivan (below).
Additional pod blasting clinics will
take place on Sep 16 at Carolina Easter, Courtland, VA; Sep 18 at Meherrin Ag.
& Chemical, Capron, VA; Sep 22 at TAREC, Suffolk, VA; Sep 23 at Carolina
Eastern, Courtland, VA; Sep 25 at Meherrin Ag. & Chemical, Newsoms, VA; and
Sep 28, at Indika Farms Inc, Windsor, VA. They are organized by Extension
Agents Livvy Preisser, Elisabeth Pittman, and Josh Holland.
Because temperatures of the past 3
weeks seem to decrease in the next 3 weeks and into the Fall by 15 to 20 F
daily, from high 80s and on some days mid-90s to only mid-70s, the rate of pod
development from immature (white mesocarp color) to mature (brown and black
color) will decrease as well. Therefore, patience is needed with peanut crop this
Fall for harvesting high yields and SMK in Virginia.