By: Tom Kuhar (Entomology Professor, Virginia Tech), Kadie Britt (Ph.D. student researching hemp IPM), and Helene Doughty (Entomologist, Eastern Shore AREC, Painter, VA)
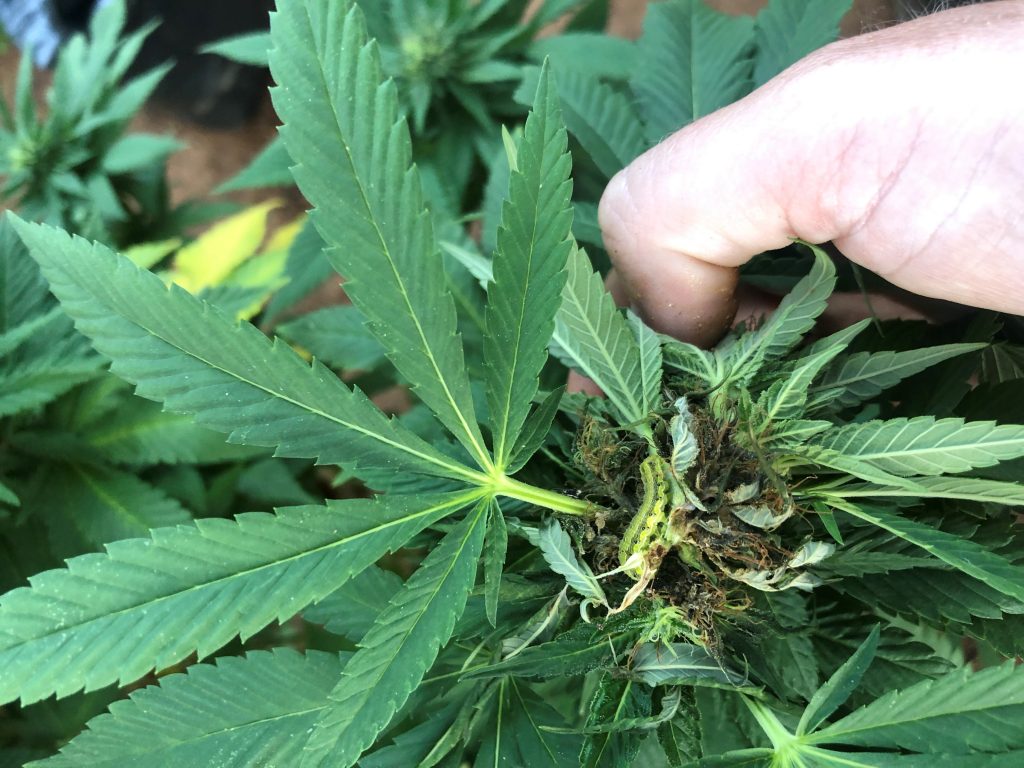

Corn earworm has become one of the most important pests of hemp, Cannabis sativa, in Virginia and many other states (Fig. 1). Please see our factsheet on this insect as it relates to hemp: https://www.pubs.ext.vt.edu/content/dam/pubs_ext_vt_edu/ENTO/ento-328/ENTO-328.pdf
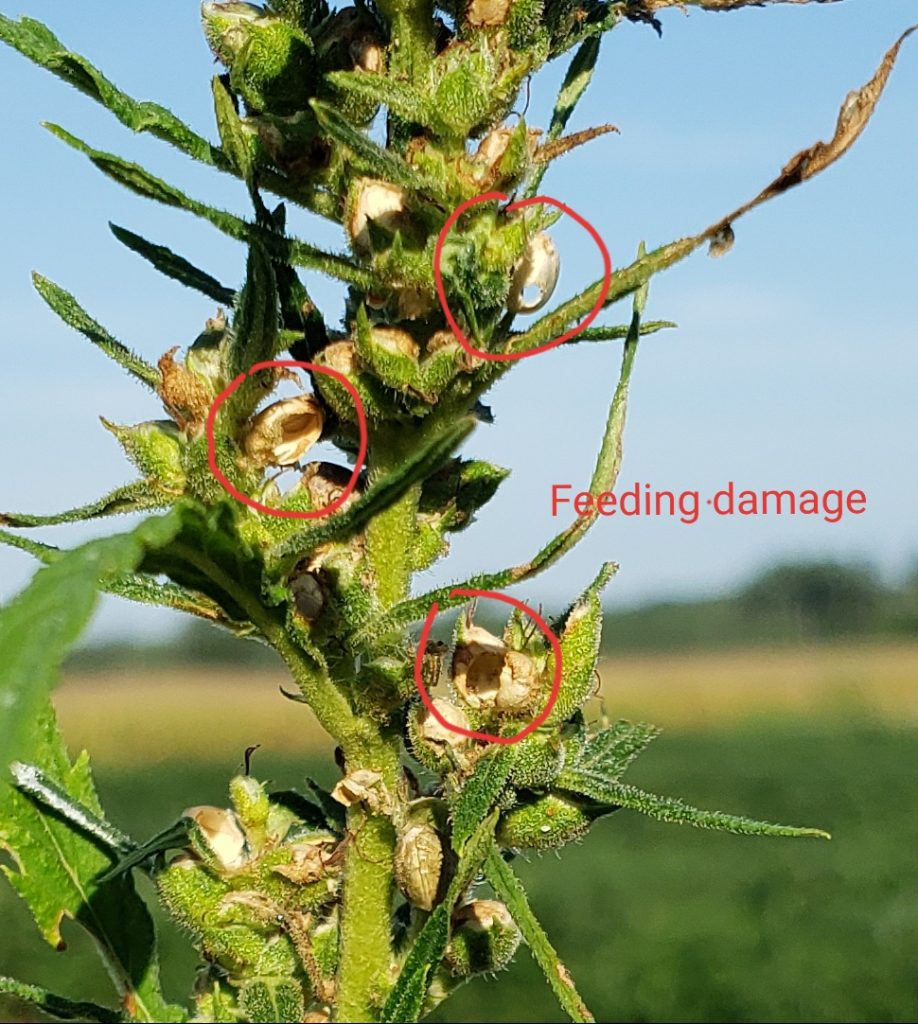
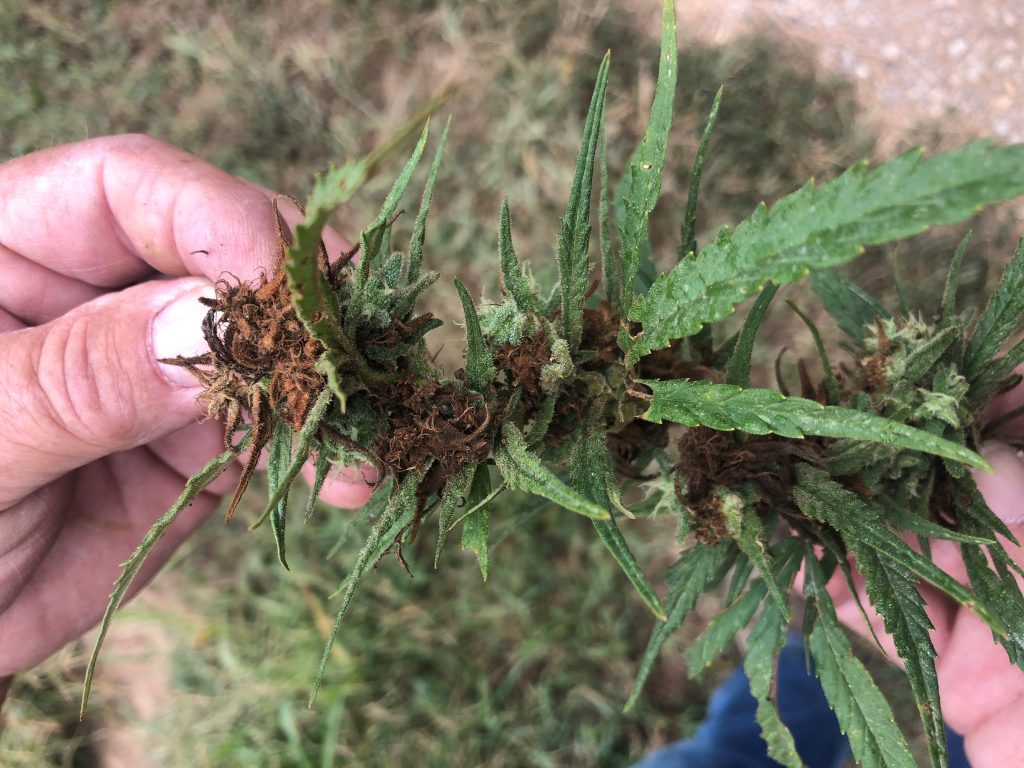
Corn earworm can be quite damaging to the seed heads of hemp grown for grain (Fig. 2), but, as we’ve seen recently in Virginia, the pest can also damage hemp grown for CBD oil. Over the past few weeks, corn earworm densities and damage to CBD hemp has reached very high levels throughout Virginia, and their presence in fields has been associated with increased flower bud rot (Fig. 3). This can result in significant economic damage to that crop.
Due to strict regulations on pesticide use on hemp, insecticide recommendations for managing this pest are quite limited at this time. Recently, we evaluated the efficacy of some naturally-derived pesticides that can be legally applied on hemp in Virginia and one naturally-derived (OMRI-certified) insecticide that currently is not allowed to be applied on hemp (Spinosad).


Eastern Shore Insecticide Field Trial:
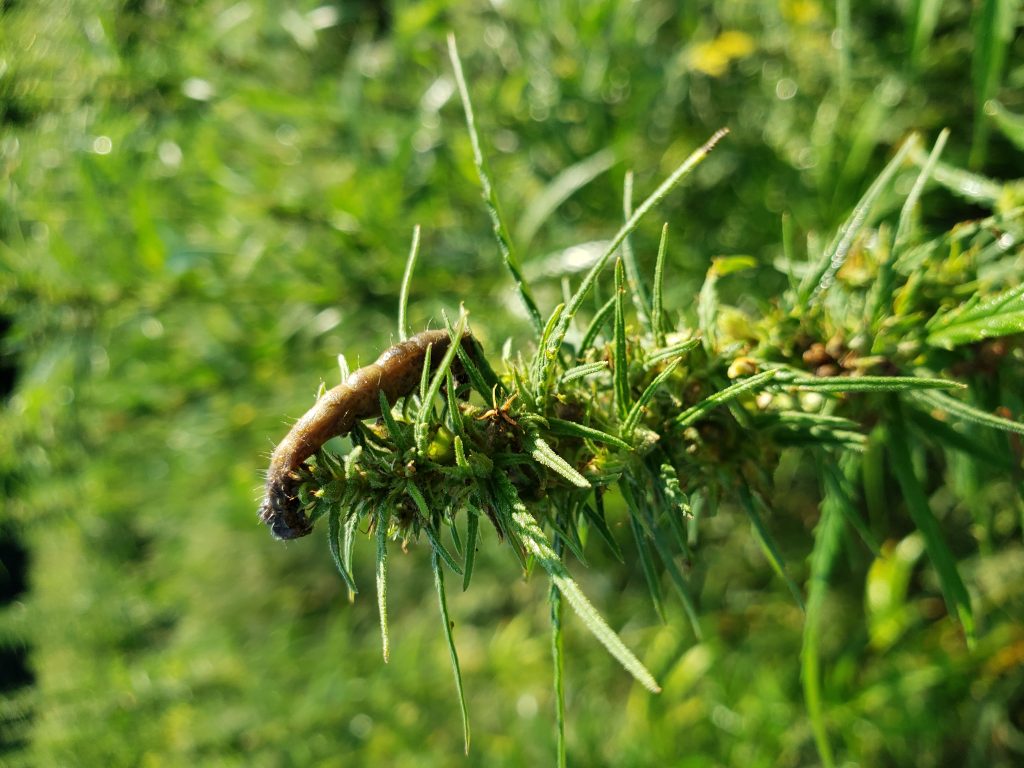
- Gemstar (5 fl oz/A) – which is a nuclear polyhedrosis virus that is specific to the corn earworm species. The virus causes corn earworm to become sick and die. Fig. 4. Shows a corn earworm killed by the virus.
- Javelin WG (8 oz/A) – Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) strain kurstaki – bacterial crystalline proteins that kill caterpillars.
- Dipel DF (16 oz/A) – Bt kurstaki different formulation
- BoteGHA (32 fl oz/A) – Beauveria bassiana – entomopathogenic fungi
- Entrust (5 oz/A) – Spinosad derived from soil microbes. *cannot legally be applied on hemp in Virginia.

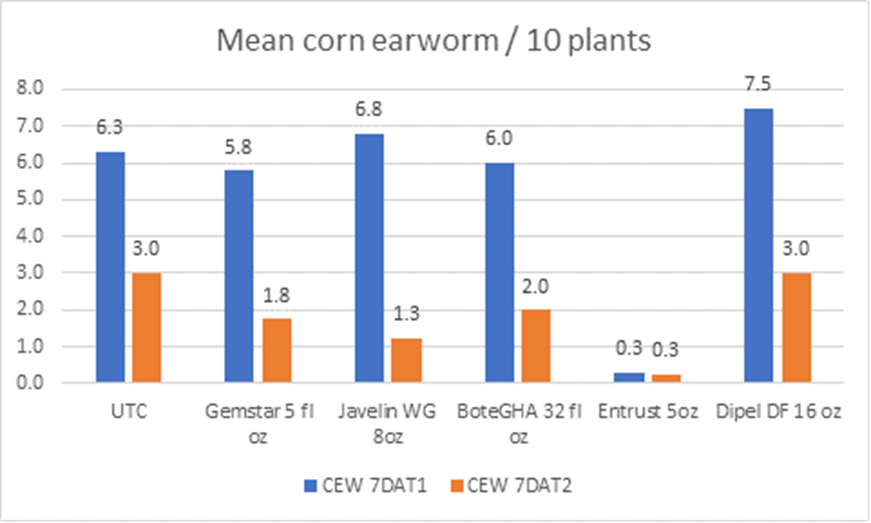
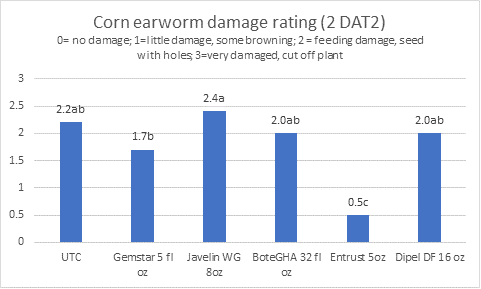
We evaluated their efficacy in the field on the Eastern Shore of Virginia in a randomized complete block small plot trial. Hemp plots were sprayed twice (1 week apart) and numbers of live CEW larvae and damage was assessed. Results are shown in Figs. 5 & 6. Entrust was the only product that provided effective control of CEW. Unfortunately, this is the one product that we evaluated that is not allowed to be applied on hemp. The insecticide Entrust is OMRI-certified however.
Virginia Tech bioassay trial:
Treatments included:
- Gemstar (5 fl oz/A) – which is a nuclear polyhedrosis virus that is specific to the corn earworm species. The virus causes corn earworm to become sick and die. Fig. 3. Shows a corn earworm killed by the virus.
- Javelin WG (8 oz/A) – Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) strain kurstaki – bacterial crystalline proteins that kill caterpillars.
- Dipel DF (16 oz/A) – Bt kurstaki different formulation
- Xentari (16 oz/A) – Bacillus thuringiensis , subsp. aizawai , Strain ABTS-1857
- BoteGHA (32 fl oz/A) – Beauveria bassiana – entomopathogenic fungi
- Entrust (5 oz/A) – Spinosad derived from soil microbes. *cannot legally be applied on hemp in Virginia.
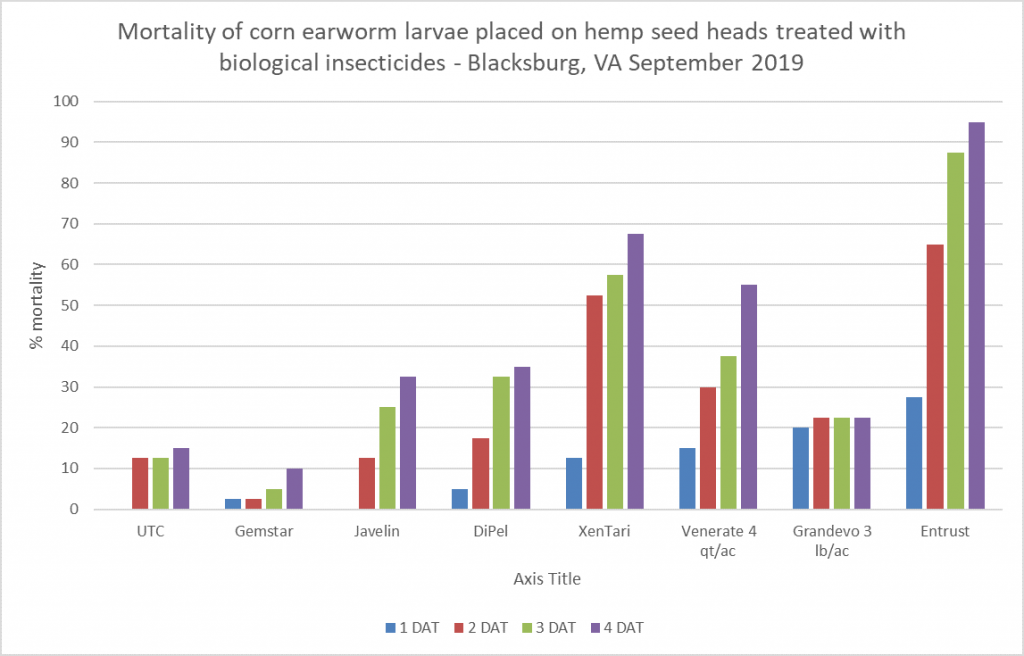
In order to evaluate the efficacy, untreated hemp seed heads were collected from Kentland Farm and dipped in each of the treatments. Approximately 1 oz of seeds was placed per diet cup and four reps of 10 cups each were set up for the aforementioned six insecticide treatments. CEW larvae (3rd instar (medium sized) were collected from sweet corn planted at Kentland Farm and were immediately placed 1 larva per cup. Mortality was evaluated 1, 2, 3, and 4 days after treatment (Fig. 7). Similar to the Eastern shore field trial, Entrust provided the most effective control of CEW. However, this trial also included the Bt aizawai product Xentari, which also provided significant control (better than the other products except spinosad. Xentari is allowed for use on hemp in Virginia. For best management of corn earworm during this time, apply Bt products on hemp every few (2-3) days in early morning or late evening. Corn earworm must consume the insecticide for the application to be effective, so ensure good spray coverage on plants. Dead worms may not be noticed until 48 hours after first application.

Pingback: How to Enhance Communication and Make Your Research More Accessible