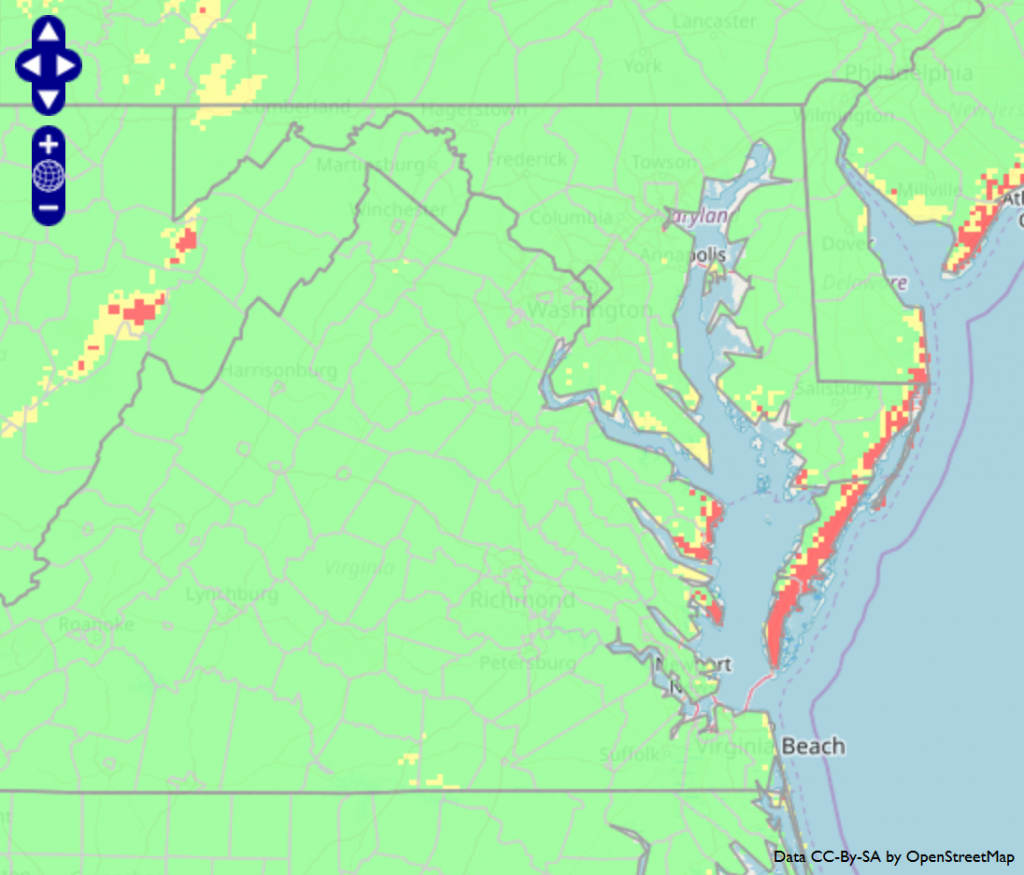
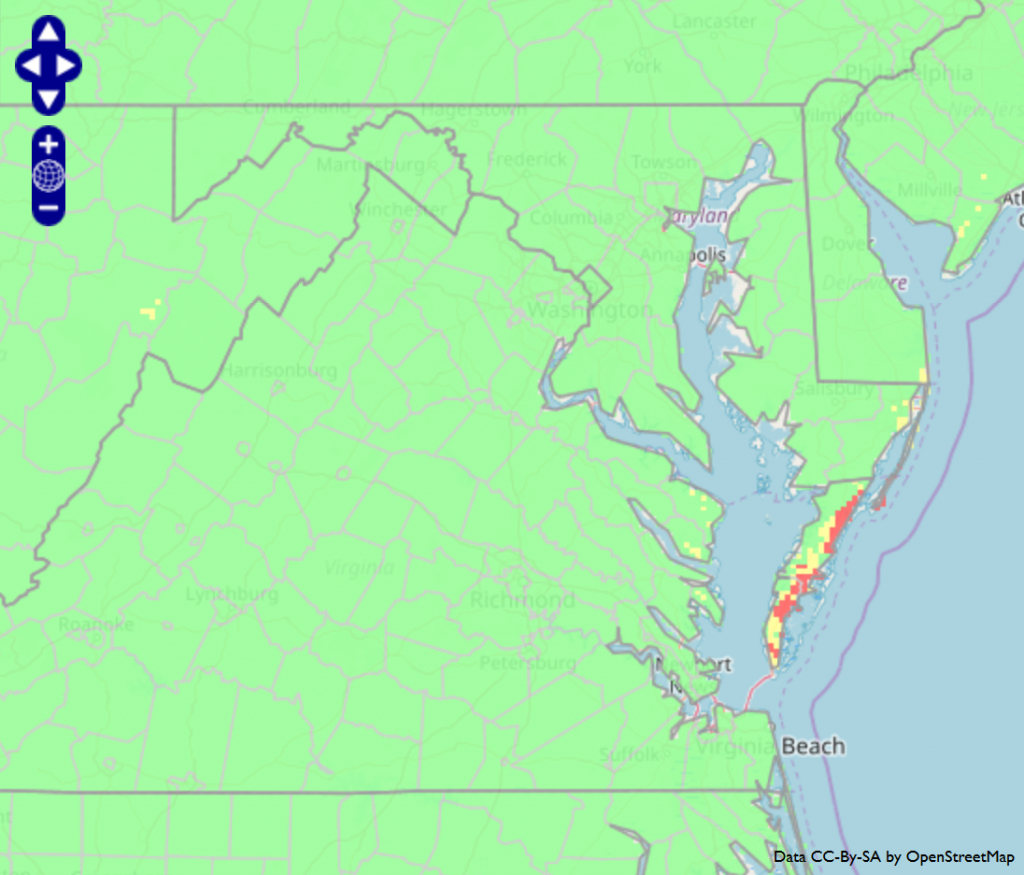
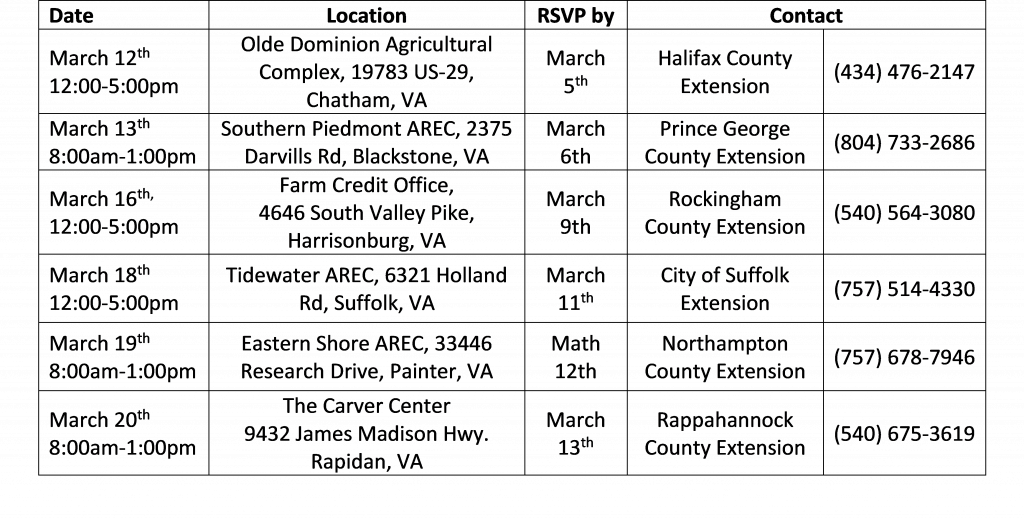Yield reductions in small grains can result from cereal leaf beetle larvae feeding on leaf photosynthetic tissue. Infestations in Virginia are sporadic, but if you scout for them I wanted to share the following information. A temperature-based model indicates that Suffolk (Virginia) will reach the egg peak for this pest on March 22, 2024 (that’s the day when 182 degree days have accumulated). The model uses January 1 as a biofix; a lower development threshold of 8℃, and an upper development threshold of 25℃.
Eggs are yellow-orange, elliptical, about 1/32-inch long, and are often found along the midvein of the leaf.
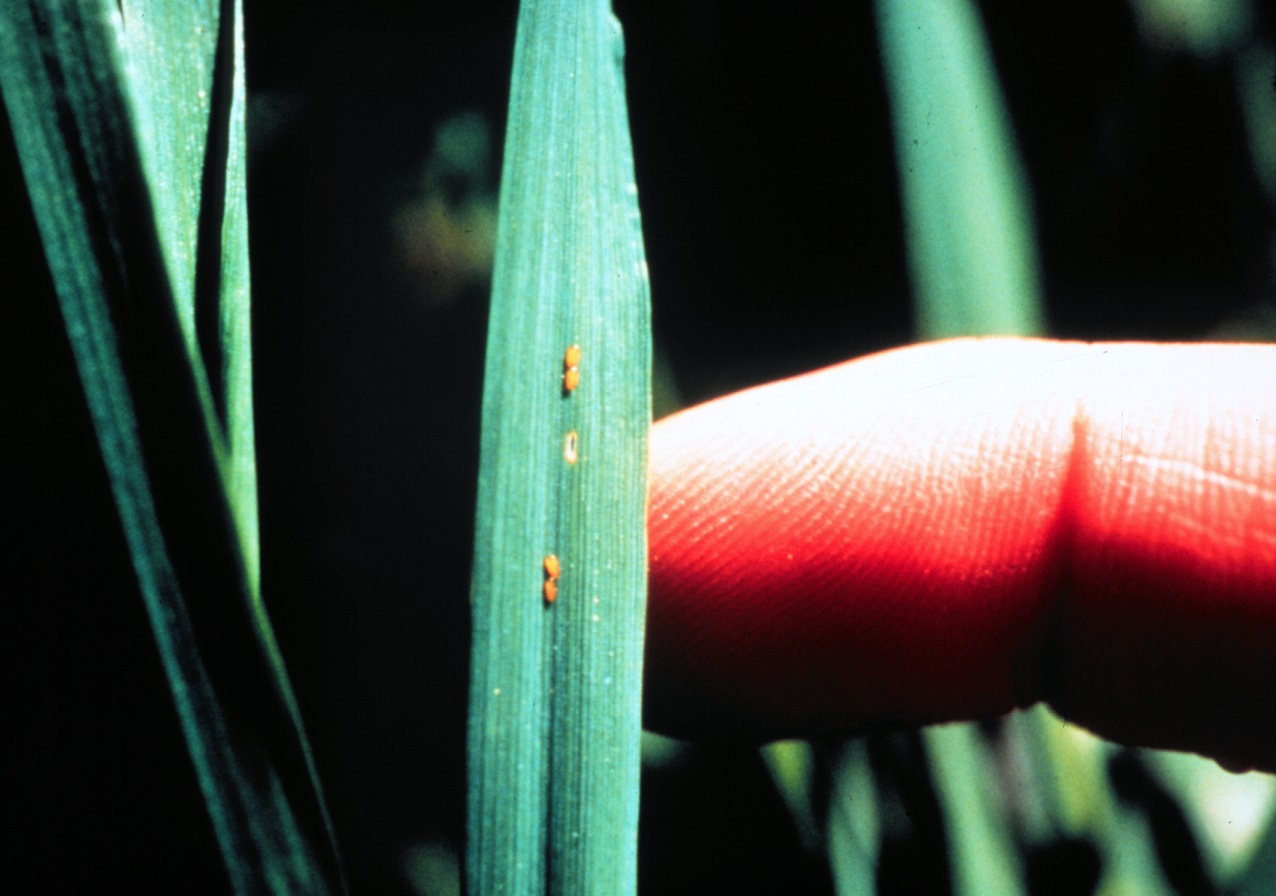

The larval peak follows the egg peak by an average of 17.5 days, which is predicted to fall during the second week of April for Suffolk.
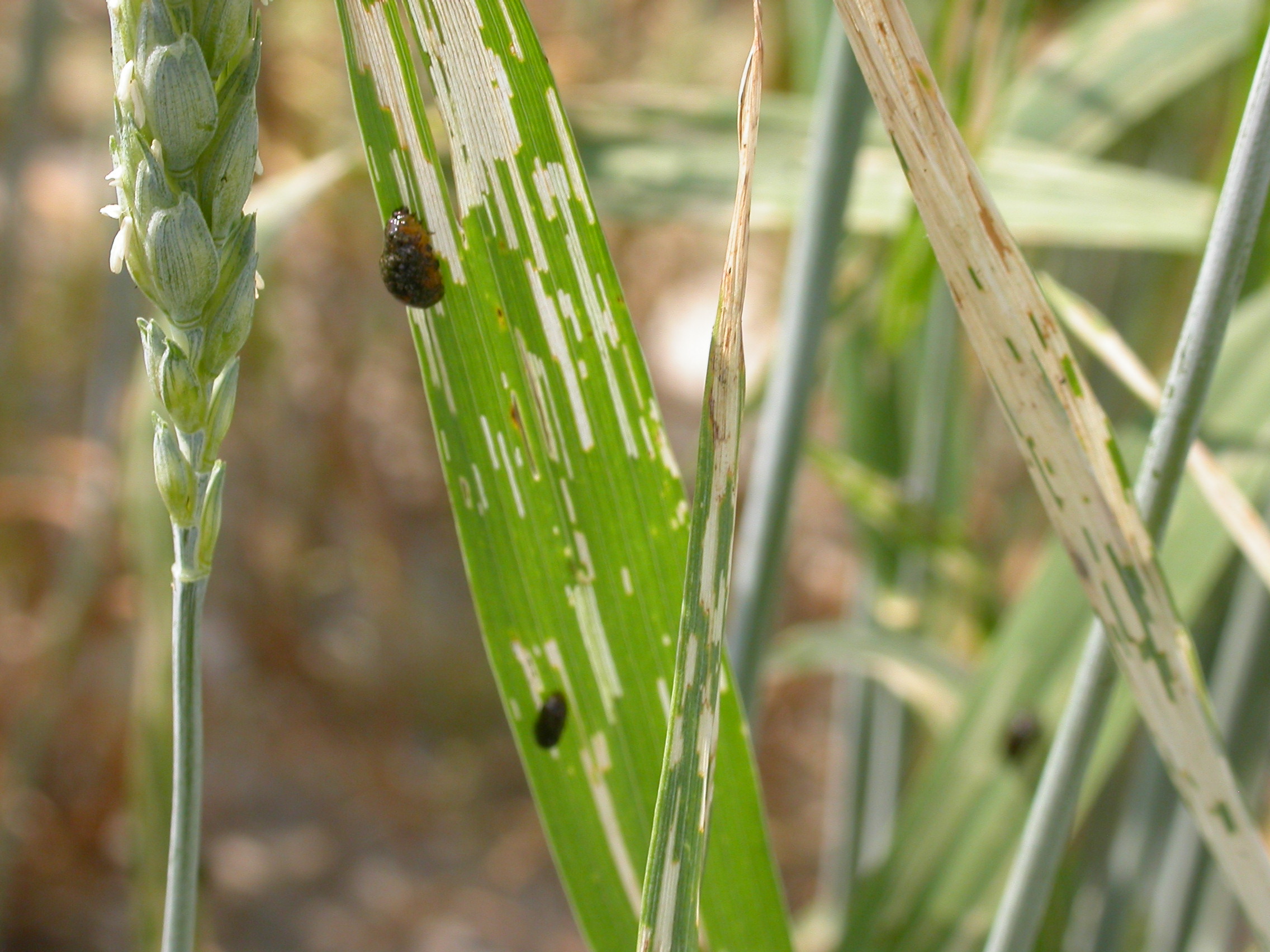

To scout for cereal leaf beetle, inspect 10 tillers (stems) in at least 10 different sites. If you are seeing mostly eggs, you should scout again in 5-7 days when some have hatched into small larvae. The eggs may be parasitized. Virginia’s threshold is 25 eggs + small larvae (total) per 100 tillers. At least half of that 25 should be larvae. An insecticide spray, if needed, should target the newly-hatched larvae. There is only one generation per year.