Early season scouting (pre-bloom cotton)
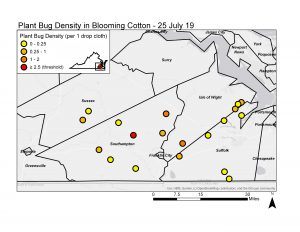
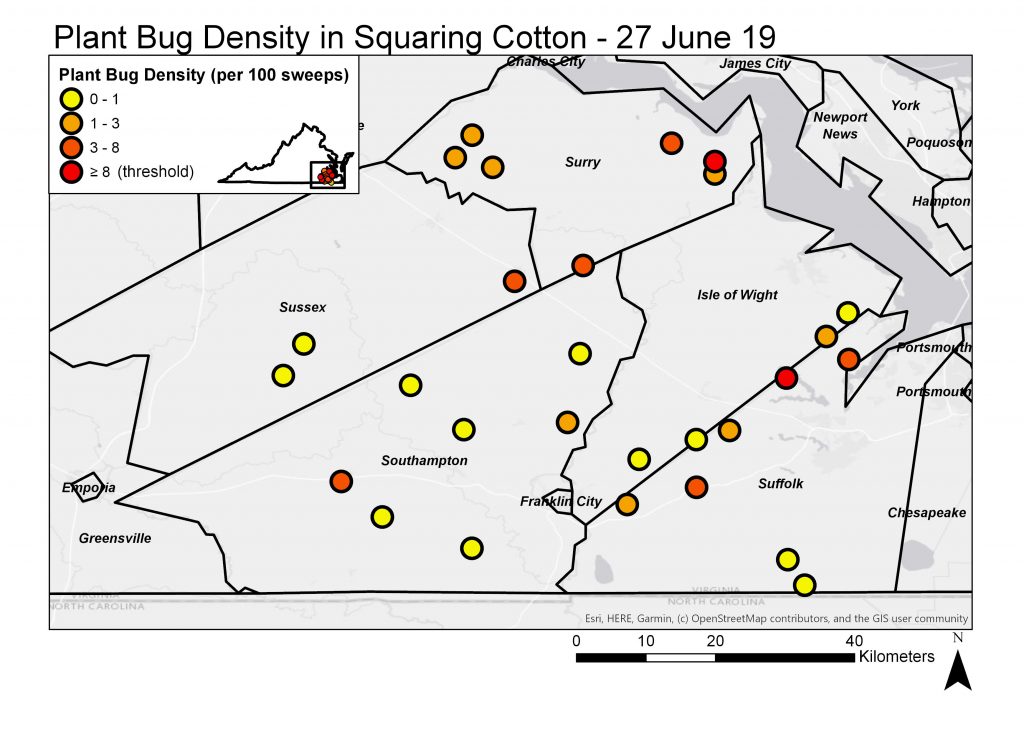
We recommend scouting for plant bugs as soon as cotton begins squaring. We encourage everyone to scout for plant bugs, especially those that saw high numbers last year. Early in the growing season (pre-bloom) we are scouting for adult plant bugs immigrating into cotton from flowering weedy hosts and other cultivated hosts nearby (corn, wheat, soybean). Plant bug adults (pictured below) are approximately 5-6mm in length (quarter inch) and can be identified by their yellowish brown body color, conspicuous “Y” shape on their scutellum or upper back, and two yellow dots on their cuneus or lower back. For pre-bloom cotton, we recommend sweep net sampling with an action spray threshold of eight plant bugs (adults and nymphs) per 100 sweeps. This can be done by conducting four to eight random 25-sweep samples throughout each field. We also recommend measuring square retention before bloom by sampling 25 random plants in each field and calculating the percentage of missing or black squares from all first positions on whole plants or the top five nodes. Consider a spray application for plant bugs if the insect threshold is reached (8 plant bugs per 100 sweeps) and square retention is below 80 percent.
Click on this video link to see sweep net sampling technique in cotton.

Plant bug pre-bloom action threshold in cotton.
Mid- to late-season scouting (flowering cotton)
For mid- to late-season scouting, when cotton is flowering, we are mainly sampling for plant bug nymphs using a black drop cloth. The action threshold for triggering sprays in flowering cotton is 2-3 plant bug nymphs and adults per drop cloth sample. For drop cloth sampling, we recommend placing the drop cloth in between two rows and vigorously beating plants onto the drop cloth. We also recommend taking at least four samples per field.
Click on this video link to see drop cloth sampling technique in cotton.

Plant bug action threshold in flowering cotton.
Insects often mistaken for plant bugs
Common insects in cotton fields that are often confused with plant bugs include big-eyed bugs, aphids, and stink bug nymphs (pictured below). Big-eyed bugs head and eyes are wider than their body. Aphids are a secondary pest and are generally smaller and slower than plant bug nymphs with two tailpipes or cornicles on their lower back. Stink bug nymphs have a more shield-like body shape with three black stripes on their antennae.

Insects that are often confused with plant bugs include big-eyed bugs, aphids, and stink bug nymphs.
Economic benefits of managing plant bugs in cotton
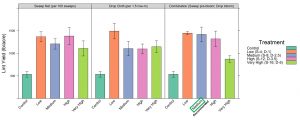
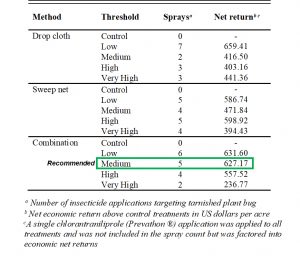
The single most important management strategy for plant bugs in cotton is applying insecticides at the recommended action thresholds described above. The bar graph below highlights lint yield gained when applying insecticides at various thresholds (low, medium/recommended, high, very high) using sweep net only, drop cloth only, or both (as described above). We see that the highlighted recommended threshold using sweep net sampling pre-bloom and drop-cloth sampling during flowering was one of the highest yielding treatments with the highest economic returns among treatments with five or fewer spray applications. The major take-home from these data is that any scouting technique (sweep net and or drop cloth sampling) at any threshold, is going to significantly increase lint yield and economic returns when plant bug infestations are present!

Bar chart highlighting lint yield gained above the untreated control using various sampling techniques and spray thresholds for plant bugs.

Economic returns above the untreated control when properly managing cotton for plant bugs.