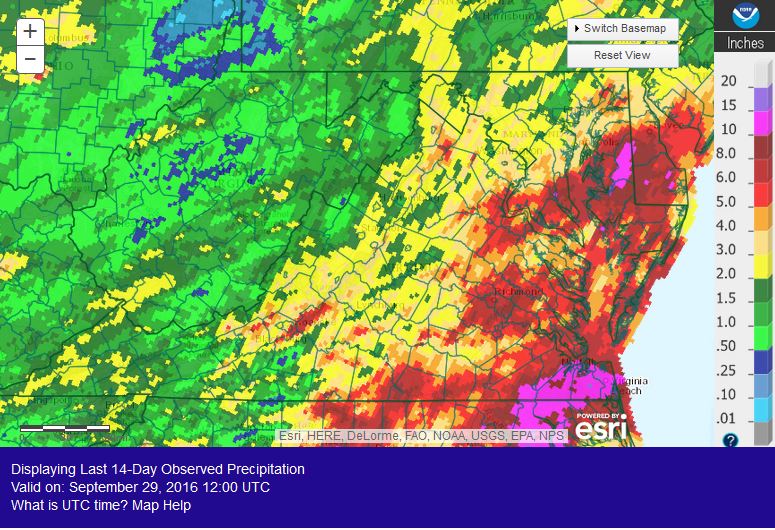
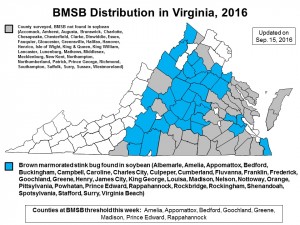
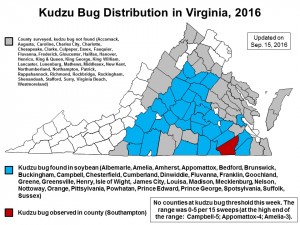
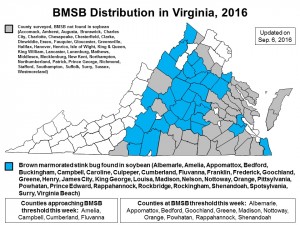
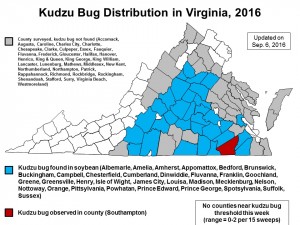
English boxwood defoliated by the boxwood blight pathogen following introduction of infected container plants on the patio. (Photo by A. Bordas)
Recent outbreaks of boxwood blight, caused by the fungus Calonectria pseudonaviculata, are causing concern in Virginia. Boxwood blight can cause severe defoliation of susceptible boxwood, including English and American boxwood, and is of serious consequence to nursery growers, landscapers and homeowners. All diagnoses of boxwood blight in home landscapes made by the Virginia Tech Plant Disease Clinic since last fall are linked to new boxwood purchased from several Virginia locations of one national retailer, and new cases are likely to emerge. (See news article at: http://www.newsadvance.com/news/local/boxwood-blight-hits-lynchburg/article_a2860e97-438c-523a-9c63-202902eaf42b.html).
We strongly recommend that growers purchase boxwood from a nursery or retail outlet that has purchased boxwood exclusively from a boxwood producer in the Boxwood Blight Cleanliness Program (http://www.vdacs.virginia.gov/plant-industry-services-boxwood-blight.shtml). These producers follow stringent practices to avoid the introduction of this disease to their nurseries and are subject to followup inspections by the Virginia Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services.

Black streaking on green stems of boxwood plant with boxwood blight. (Photo by A. Bordas)
Symptoms of boxwood blight include leaf spots, black streaking on stems and severe defoliation. Other diseases of boxwood, such as Volutella blight and root diseases, can be confused with boxwood blight; therefore, laboratory confirmation is necessary. Learn to recognize symptoms of boxwood blight by viewing the image gallery on the Virginia Boxwood Blight Task Force web site (http://www.ext.vt.edu/topics/agriculture/commercial-horticulture/boxwood-blight/). Information on best management practices, resistant boxwood cultivars, and sanitizers for cleaning tools is also available on the web site.
In all the cases of boxwood blight diagnosed by the VT Plant Disease Clinic in home landscapes, the disease was introduced on infected boxwood plants. The fungus has sticky spores and is not adapted for movement on air currents; however, spores may stick to and be transported by spray hoses, tools, clothing, shoes, and vehicles. The fungus can also be transported in soil and likely by animals moving through infected plants, e.g. deer, dogs. Infected boxwood may also be present in holiday greenery.
If you suspect boxwood blight, collect symptomatic branch samples with at least a few green leaves still attached. Double bag the samples in sealable bags and take them to your local Virginia Cooperative Extension office (http://www.ext.vt.edu/offices/index.html). Samples will be forwarded to the Virginia Tech Plant Clinic for diagnosis.