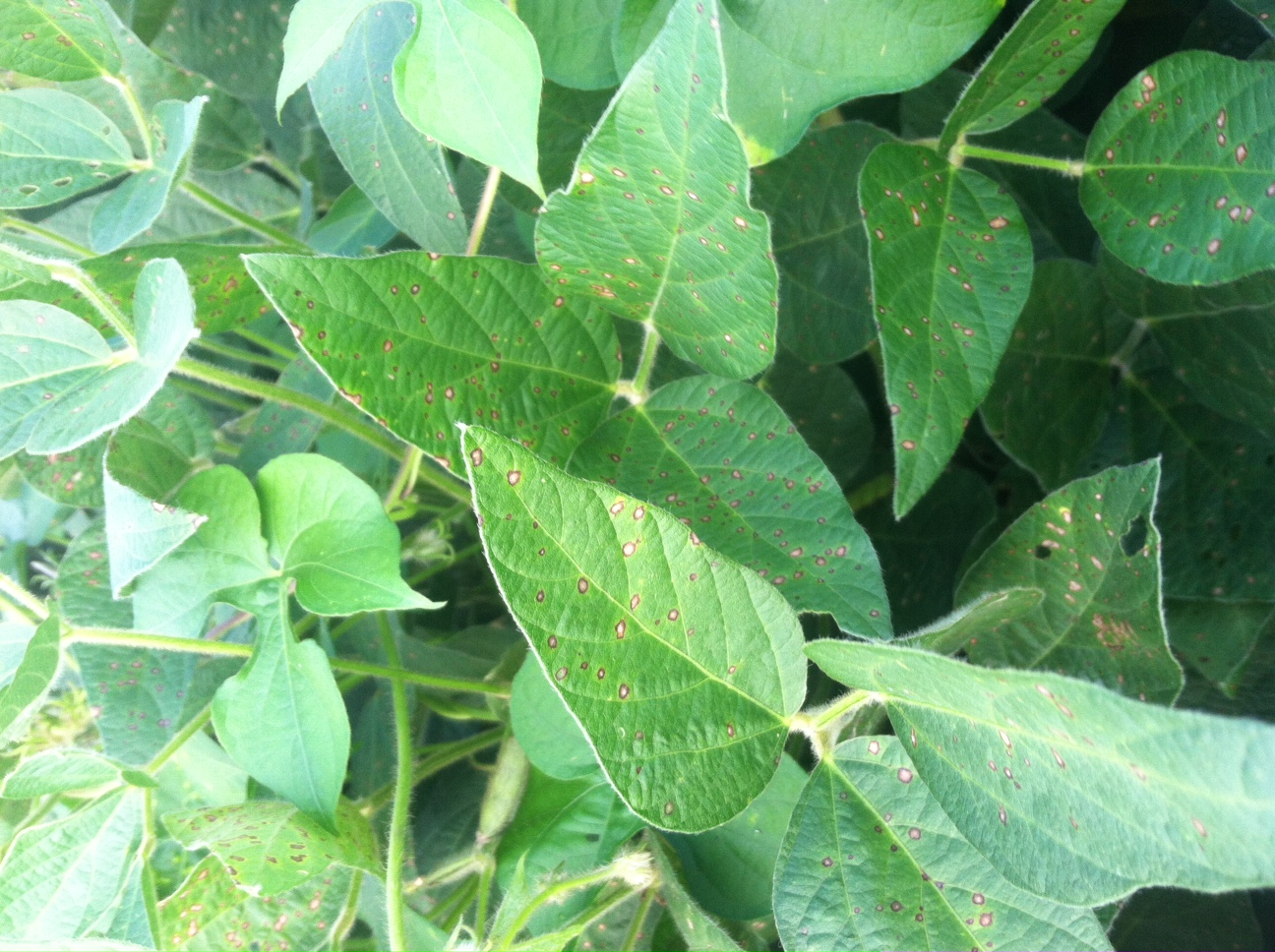
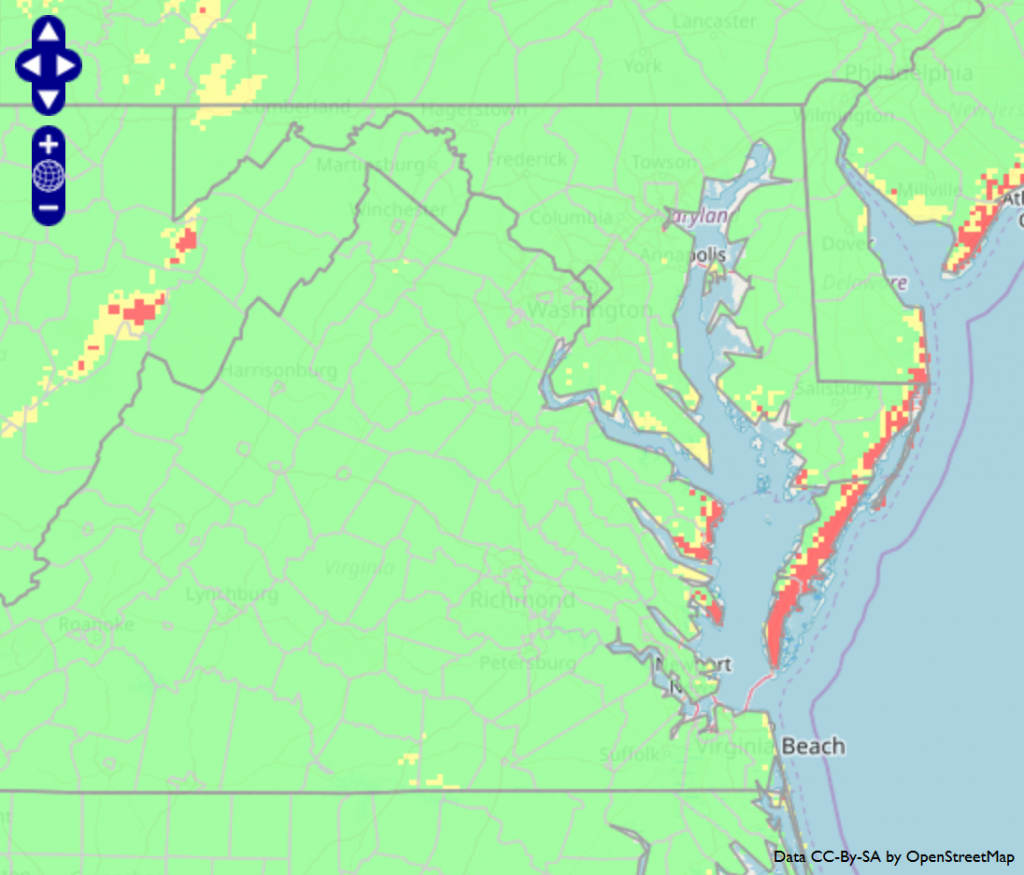
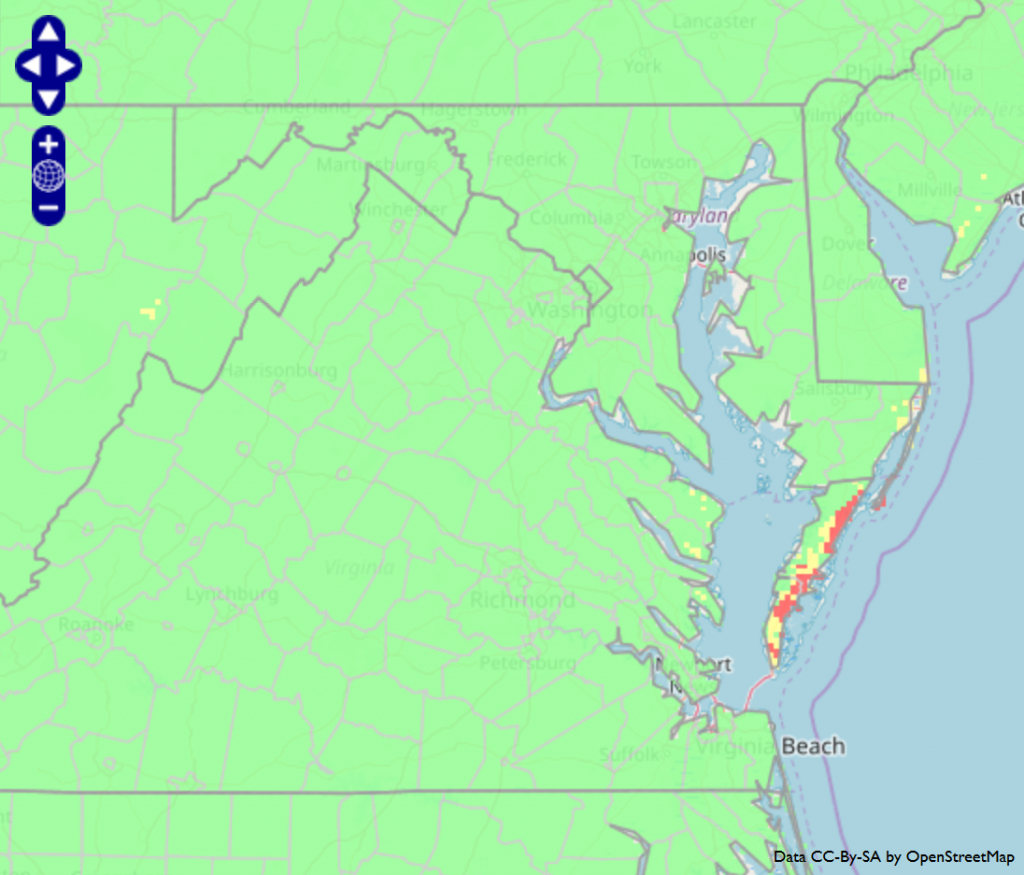
For soybean that is at or near the beginning pod (R3) stage, it is time to consider whether or not a fungicide application is needed to control foliar diseases and protect yield. The Virginia soybean fungicide advisory indicates that disease risk is moderate to high in most locations. Fields with moderate risk should be scouted since foliar diseases will not be an issue in every field every year. Keep in mind that other risk factors also contribute to disease severity and yield loss to fungal diseases. High risk fields include those where susceptible soybean varieties are planted, there is a recent history of soybean foliar diseases, and/or rotations out of soybean are short or soybean is planted continuously over several years. If based on the soybean fungicide advisory or other factors you decide to apply a fungicide, applications are generally the most effective when applied between R3 and R4 stages (no later than R5). The most recent Soybean Fungicide Efficacy Table and instructions on how to use the Virginia soybean fungicide advisory can be found in last week’s blog post. A summary of disease risk and spray recommendations for different locations in Virginia can be found below.
| Region of Virginia | Location of weather station | Soybean disease risk | Recommendation |
| Eastern Shore | Painter | High | Spray |
| Southeastern | Suffolk | Moderate | Scout |
| Southeastern | Virginia Beach | Moderate | Scout |
| Northern Neck | Warsaw | Moderate to high | Scout |
| Central | Blackstone | Low to moderate | Don’t spray |
| Northern | Middleburg | Moderate to high | Scout |
| Northern | Shenandoah | High | Spray |
| Northern | Winchester | Moderate | Scout |
| Western | Critz | High | Spray |
| Western | Blacksburg | High | Spray |
| Western | Glade Spring | High | Spray |
For detailed daily advisories, select the location closest to your field and download the corresponding file here:
If you have any questions, feel free to contact Dr. Hillary Mehl (hlmehl@vt.edu).