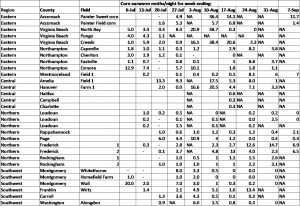
Please see the attached table for current black light trap captures of corn earworm moths: BLT_6_Sep_2018
Sweet Corn IPM Moth Trapping in Virginia – Week Ending September 7, 2018
This will be final trap catch alert of the year for the sweet corn IPM program as most corn has been harvested. I want to thank all of the VCE Extension folks who monitored traps on farms in their respective counties this year: Phil Blevins (Washington Co.); Chris Brown (Franklin Co.); Jason Cooper (Rockingham Co.); Ursula Deitch (Northampton Co.); Helene Doughty (Eastern Shore AREC Entomologist, Accomack Co.); Roy Flanagan (VA Beach); Bob Jones (Charlotte Co.); Kenner Love (Page and Rappahannock Co.); Laura Maxey Nay (Hanover Co.); Steve Pottorff (Carrol Co.); Stephanie Romelczyk (Westmoreland Co.); Beth Sastre-Flores (Loudoun Co.); Laura Siegle (Amelia Co.); Rebekah Slabach (Halifax Co.); and Mark Sutphin (Frederick Co.).
Click on the table below to view the trap catch results (moths per night) for some of the locations around Virginia for this final week. We will send out a synopsis of the season this winter. We are still seeing some high corn earworm moth activity on the Eastern Shore of Virginia, Westmoreland County on the Northern Neck, and Frederick County in the northwestern portion of our state. With the hot weather that we’ve experienced the past 2 weeks, moth activity has probably been a little higher than usual for September. Sweet corn growers are advised to keep control measures (spray intervals) as they were during August in most counties.
We still have caught very few fall armyworm moths in our traps around Virginia; however, this insect could contribute to some infestations in the ears of late corn. In an effort to fend off any more pyrethroid insecticide resistance development in our corn earworm populations, rotating to another insecticide than a Class 3 (pyrethroid) is highly encouraged for at least one spray. Diamide insecticides such as Coragen or Besiege, the carbamate Lannate LV, or the spinosyn Blackhawk, are all effective non-pyrethroid options.
Mid-Atlantic Crop Management School Registration is Open!
 Registration is open for the 2018 Mid-Atlantic Crop Management School for Certified Crop Adviser, Nutrient Management, and Pesticide Applicator Credits for Virginia, Delaware, Maryland, West Virginia, and Pennsylvania. The venue is the Princess Royale Oceanfront Hotel and Conference Center in Ocean City, MD on November 13-15, 2018. Register early so you can enroll in your preferred classes!
Registration is open for the 2018 Mid-Atlantic Crop Management School for Certified Crop Adviser, Nutrient Management, and Pesticide Applicator Credits for Virginia, Delaware, Maryland, West Virginia, and Pennsylvania. The venue is the Princess Royale Oceanfront Hotel and Conference Center in Ocean City, MD on November 13-15, 2018. Register early so you can enroll in your preferred classes!
Registration: https://app.certain.com/profile/2876563
Schedule: https://sites.udel.edu/agronomy/cropschool/
Finishing out the soybean crop – when you can safely stop spraying
Soybean loopers have reared their ugly heads across southeastern and coastal Virginia this week. With many of us busy hauling corn, it is reasonable to ask – when can we stop spraying beans?
In a normal year, we could safely ignore mid-September infestations. This year, the majority of double crop Virginia fields are completing pod fill. Research indicates that R3-R5 beans benefit from a spray when defoliation reaches 15% and you find more than 1 looper per sweep. I recommend that you at least double, and can safely triple, this threshold in R6 beans (i.e., 35-50% defoliation is acceptable). It benefits you to exercise restraint when treating fields after R5.5. There is no scenario when you need to spray R7 beans for loopers. Cooler evening temperatures will work in our favor when they arrive.
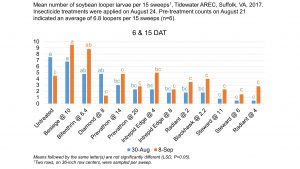
In Virginia, Intrepid Edge and Steward have been our most consistent treatments (see image below from 2017). Looper populations in Virginia have tested diamide resistant the past two years (e.g., Besiege, Prevathon). Spraying pyrethoids will only make the problem worse.
Finishing Out the Soybean Crop – What do we need for Good Yields?
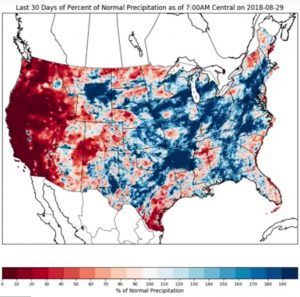
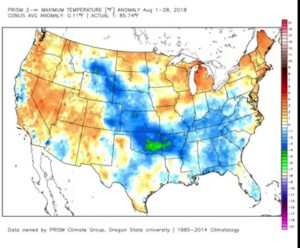
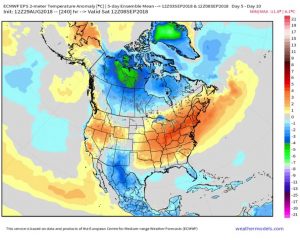
In general, we’ve had a good, but not great year for soybean in Virginia. Although many areas were hit with a 3 to 4 week dry spell during July, August rains kept us in the game. However, we did not see the ample rains or cool temperatures that we experienced in August of 2017, which resulting in record yields. Below is a summary of August rainfall and temperature anomalies for the U.S.
As you’ll notice, we had about average or slightly below average precipitation and average to slightly above average temperatures for most of Virginia’s soybean growing areas.
So, I do not suspect that our yields will be as good as last year. Still, our earlier-maturing varieties planted in April or May should yield quite respectably considering that most have made over 50% of their yield – they have reached the R6 stage (see photo below). Yield of our later-maturing varieties, planted in May and early June, and our double-crop plantings are not quite there yet – much of our yield is yet to be determined – R5 soybean have only made roughly 25% of their yield at that time.
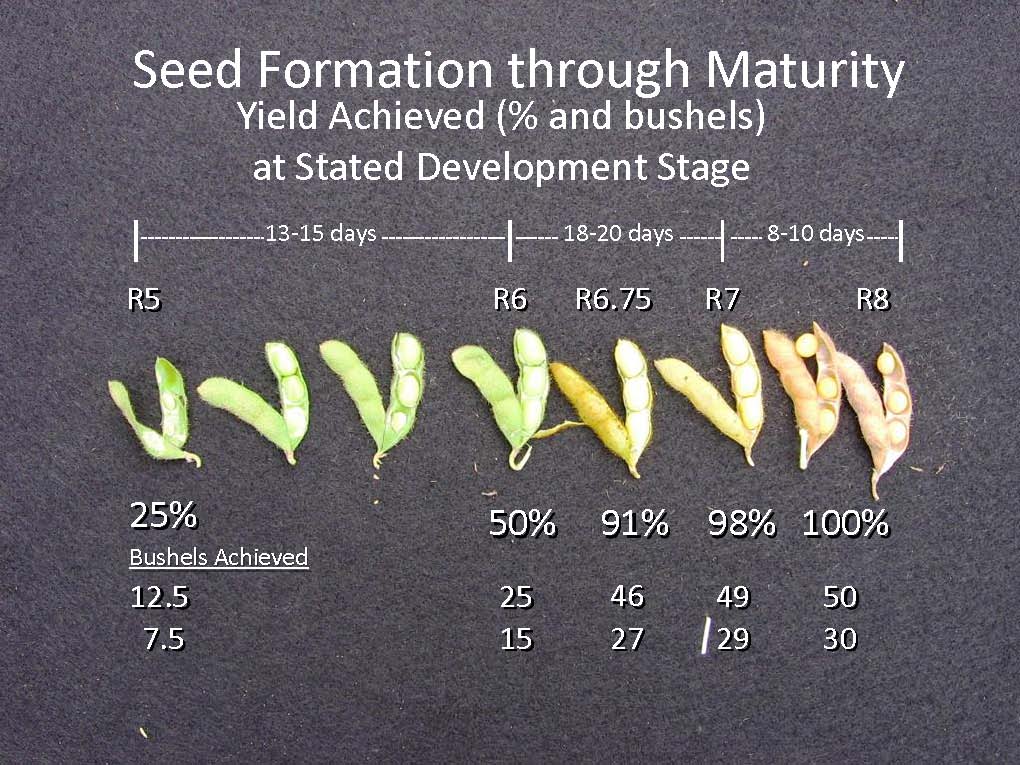 So, what do we need for good yields? Rain is obvious. Full-canopied plants with adequate soil moisture will draw about 0.25 inches of water/day from the soil. But, we also need cool temperatures – soybean do not generally like 90+ degree days, especially when forming seed.
So, what do we need for good yields? Rain is obvious. Full-canopied plants with adequate soil moisture will draw about 0.25 inches of water/day from the soil. But, we also need cool temperatures – soybean do not generally like 90+ degree days, especially when forming seed.
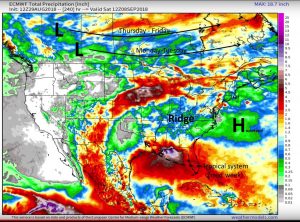
Below is the 10 day rainfall and temperature forecast for the U.S., and it does not necessarily look good for us. Note that the rainfall is predicted accumulation and the temperature map shows anomaly. Although we should get some rain this weekend only (more in northern parts), temperatures are supposed to be above average. But, forecasts are only forecasts. The weather does change. I hope we will get the needed rainfall that they are predicting this weekend. But a big ridge appears to be setting up over the Mid-Atlantic states for next week. This usually means warm weather and only at the edges of ridges do we normally see rainfall – note the heavy rainfall predicted from Nebraska through Michigan.
I don’t mean to discourage, just to inform. We still have decent soil moisture, at least in the subsoil. With rain this weekend, we should get through next week without too much harm to the crop.
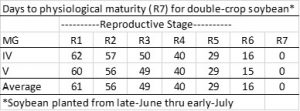
Our double-crop soybean (assuming late maturity group 4’s and group 5’s planted in late June to July) are just now in the R5 stage – it usually takes 80 to 100 days from planting to reach R6, depending on maturity and planting date. So some timely September rains will usually result in good double-crop soybean.
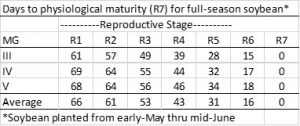
When will our yield be “made”? Below is table showing the number of days to soybean physiological maturity (R7; 95% of yield has made). When can we expect to be harvesting our soybean? Full maturity is reached about 2 weeks after R7 and harvest can proceed after the soybean have dried down to a harvestable moisture, usually within a week after R8.
Black light trap report for Aug. 30, 2018
Average nightly captures of corn earworm moths in local black light traps this week were: Hanover=1.0; Southampton=0.7; Suffolk=28.1; Warsaw=3.6; Waverly=3.7. Here is the table: BLT_30_Aug_18
2017 Virginia On-Farm Wheat Test Plots
The 2017 Virginia On-Farm Wheat Test Plots have been published and are now available on the Virginia Cooperative Extension website. For more information or a hard copy, contact Mike Broaddus, Extension Agent, at the Caroline County office.
he demonstration and research plot results discussed in this publication are a cooperative effort by seven Virginia Cooperative Extension agents, extension specialists from Virginia Tech, and a VCE summer intern. We are proud to present this year’s on-farm small grain plot work to you. We hope the information in this publication will help farmers produce a profitable crop in 2018.

Small Grain Yield Contests Show High Yields Across the Commonwealth
The Virginia Grain Producers Association is proud to announce the 2018 Virginia Wheat and Hard Wheat Yield Contest Winners.
This year’s winners come from counties across the Commonwealth and have once again proven that Virginia producers are capable of achieving exceptional yields. Yield contests, such as this, are an important element in our mission to highlight and communicate the accomplishments of Virginia agriculture to our industry partners and the general public. The top-ranked growers will be given cash prizes donated by the providers of their winning seed, and will be fully recognized with a plaque presented by one of our industry leaders at the Virginia Grains and Soybean Annual Conference next February.
At 108.6 bushels per acre, Alan Welch’s wheat took first place. Katie Myer’s hard wheat yield of 85.7 bushels per acre claimed first prize.
The hard wheat portion of the contest is sponsored by Mennel Milling to highlight the planting of hard wheat in the Commonwealth. Hard wheat is primarily used as a bread wheat. The majority of the wheat grown in Virginia is soft red winter wheat, which is used in bakery products such as flat breads, cakes, pastries and crackers.
2018 Virginia Wheat Yield Contest Winners
1st Place $700: Alan Welch, Welch Farms, Inc., Northumberland County
108.6 Bu/Acre, Pioneer 26R59
2nd Place $500: Justin Welch, Welch Farms, Inc., Northumberland County
105.5 Bu/Acre, Pioneer 26R59
3rd Place $300: Paul Davis, Davis Produce, New Kent County
89.6 Bu/Acre, AgriMaxx 463
2018 Virginia Hard Wheat Yield Contest Winners
1st Place $700: Katie Myer, Richmond County
85.7 Bu/Acre, Vision 45
2nd Place $500: Paul Davis, Davis Produce, New Kent County
78.5 Bu/Acre, Vision 45
Many thanks go out to The Mennel Milling Company of Virginia, Pioneer, AgriMaxx, and UniSouth Genetics (USG) for sponsoring the Small Grain Yield Contests.
Peanut Fall Events
Peanut Extension activities will continue this Fall. Interested to see what future peanut varieties look like? Then come here Martin Field Day Flyer. Or maybe willing to learn more on peanut production from peanut specialists, and interested in finding when is the optimum time to harvest your peanuts? Then you are welcome here VA PEANUT Upcoming Events – 2018.
Sweet Corn IPM Moth Trapping in Virginia – Week Ending August 24, 2018
Corn earworm moth catch data from sweet corn farms in Virginia can be found in the table below. In summary, corn earworm moth activity increased dramatically this week at several locations including lower Northampton County, Westmoreland County in the Northern Neck, Amelia County, Hanover County, and Frederick County. Moth activity is quite variable right now, and should certainly be monitored carefully in the coming weeks. We still have caught very few fall armyworm moths in our traps around Virginia; however, it should be noted that the Amelia County Farm averaged 5.5 FAW moths per night, which is the highest of any trap this season so far. So, a late flight of this pest appears to have reached some part of Virginia.
In an effort to fend off pyrethroid insecticide resistance development in our corn earworm populations, rotating to another insecticide than a Class 3 (pyrethroid) is highly encouraged for at least one spray. Diamide insecticides such as Coragen or Besiege (although it includes lambda-cy with the diamide), the carbamate Lannate LV, or the spinosyn Blackhawk, are all effective rotational insecticide options.
I want to once again thank Helene Doughty at the ESAREC and all of the VCE agents that are monitoring these pests on sweet corn farms in 17 different counties in Virginia: Phil Blevins (Washington Co. – See Photograph below); Chris Brown (Franklin Co.); Jason Cooper (Rockingham Co.); Ursula Deitch (Northampton Co.); Roy Flanagan (VA Beach); Kenner Love (Page and Rappahannock Co.); Laura Maxey Nay (Hanover Co.); Steve Pottorff (Carrol Co.); Stephanie Romelczyk (Westmoreland Co.); Beth Sastre-Flores (Loudoun Co.); Laura Siegle (Amelia Co.); Rebekah Slabach (Halifax Co.); and Mark Sutphin (Frederick Co.).
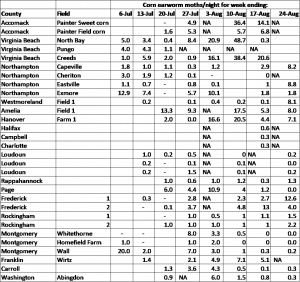
Corn earworm moth catch in pheromone-baited Heliothis traps around Virginia for week ending August 24, 2018.