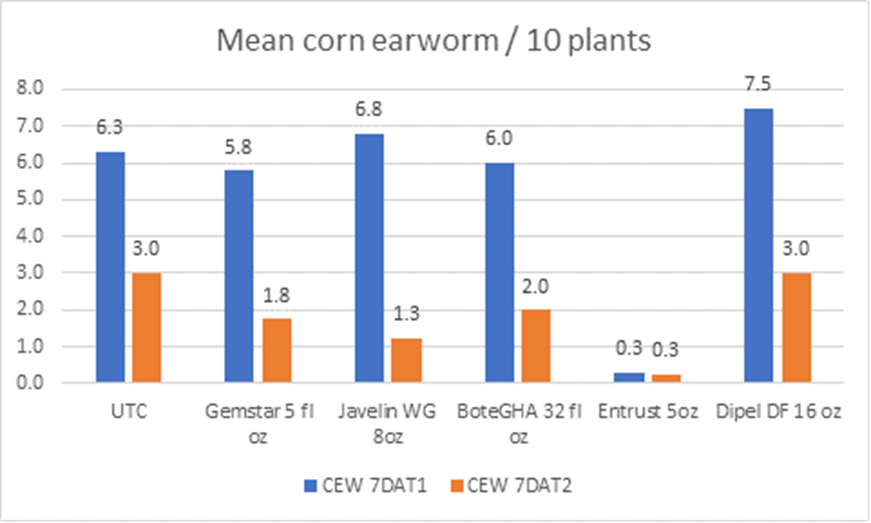
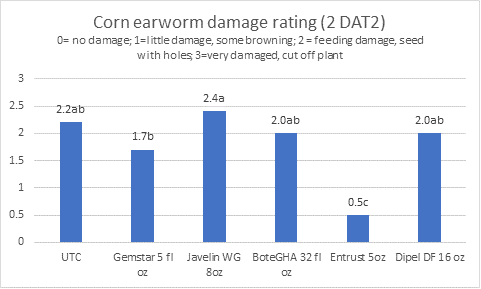
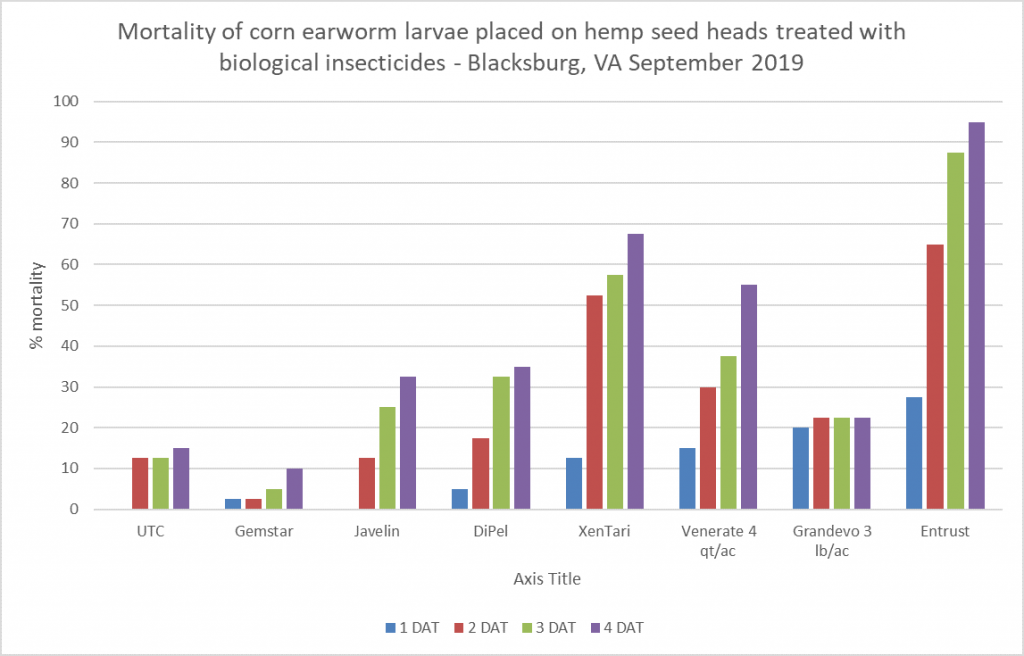
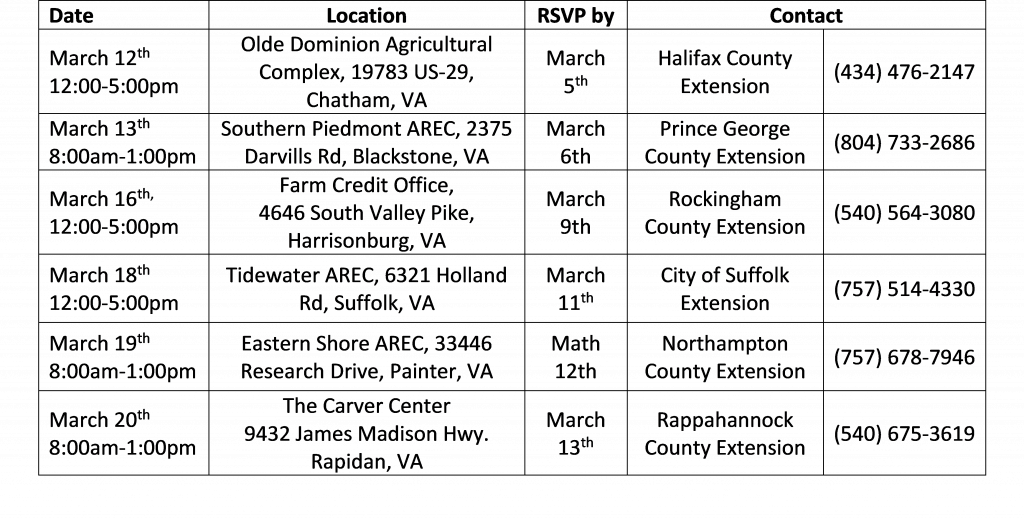The 2020 Tri-County Crop Production Conference will be held Tuesday, Jan. 14 at the Carson Volunteer Fire Department on 19806 Halifax Rd in Carson, VA. This year’s conference will host several Specialists from Virginia Tech that will cover a wide variety of topics. In addition, you will be able to get your dicamba herbicide certification with training being offered by Don Cline of BASF. We look forward to seeing your there for a great day of learning and interaction with the experts. Lunch will be provided. Agenda detail are below.
9:00 – 9:05 Welcome and Announcements
9:05 – 9:40 Positioning
Your Full-Season Soybean for Maximum Yields– Dr. David Holshouser
There are many things we can do to increase full-season soybean yield,
but decisions made before planting are the most important. This presentation will focus on
site-specifically positioning your crop to best take advantage of the limiting
resources of water, light, and nutrients.
9:40-10:20 Plant
disease management – Dr. David Langston
Nematode and disease interaction issues in soybeans. Update on fungicide and seed treatments
available for corn and soybeans. Common
diseases occurring in 2019.
10:20-10:40 Break
10:40 – 11:10 Update
on insect pest management – Dr. Sally Taylor
Review of major insect pests in 2019.
Recommendations for preparing for 2020, scouting tips to use throughout
the season, and updates on insecticides available for use.
11:10 – 11:40 Small
Grain and Corn Update – Dr. Wade Thomason
Review of the latest research in corn and small grain production in
Virginia.
11:40 – 12:00 Getting Started with Irrigation and
Irrigation Survey – Dr. Julie Shortridge
Irrigation is not used on a wide scale in Virginia. This presentation will introduce our new
water specialist and a irrigation survey for growers.
12:00 -12:45 Lunch
12:45 – 1:15 Pesticides
in VA update – Robert Christian, VDACS
Update on federal record keeping and worker protection standard.
Additional information on changes in pesticide labeling for VA. PPE review for commonly used pesticides. Changes to paraquat labeling, handling, and
training.
1:15 – 1:35 Weed
control update – Scott Reiter
Roundup resistant common ragweed is common in our soybean cropping
systems. There are also 4 different herbicide
technology systems in play for the 2020 season.
We will cover the options available and the stewardship needed to keep
the herbicides on the target crops.
1:35 – 1:55 Cover crops – Mike Parrish
Cover crops have many uses in our production systems. Soil erosion control, soil health properties,
weed control, and moisture retention.
Presentation will cover results from local cover crop plots and impact
on these properties.
1:55 – 3:00 On Target Academy – Don Cline, BASF
This session will cover the required training for using dicamba herbicide in post-emerge applications to Xtend soybeans and cotton. Applicator & recordkeeping requirements, nozzle selection and technology, buffer requirements, weather conditions, and tank mix additives will be explained in detail
Full Attendance to the conference has been approved for Private Pesticide Applicator Recertification in Commercial Categories 1A, 10, and 60.